In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relati ve risk, is the hazard ratioOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, and
1
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied
Hazard ratio odds ratio unterschied-The hazard ratio is simply the value of the hazard calculated from the treatment curve, divided by the hazard calculated from the control curve Based on the complexity, statistical software is required to make this calculation to estimate the hazard ratio Figure 1 The timetoevent curve or KaplinMeier curve13 an odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor Aside a bit of handwaving, yes the rate of occurrence



Http Aspirekpco Weebly Com Uploads 1 5 9 3 Session 6 Statistical Interpretation 19 Pdf
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Note that the adjusted odds ratio for age is lower than the unadjusted odds ratio from the previous example This is because when other predictor variables increase the odds of the response variable occurring, the adjusted odds ratio for a predictor variable already in the model will always decrease Summary Odds Ratio vs Adjusted Odds RatioIs the risk ratio or 138 telling you something different than the rate ratio of ?
The Odds Ratio Now that we have both odds, we can calculate the Odds Ratio It is the ratio of these two odds Odds runners /Odds nonrunners OR = 49/35 = 14 So the odds ratio of a Runner developing joint pain compared to a NonRunner is 14 What does the Odds Ratio mean?The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for males Now we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regressionThey carefully avoid confusing the hazard ratio with a risk ratio or relative risk The first of the three to be published (Spruance, Reid, Grace, Samore, 04) point out that, when hazards are proportional, "the hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first" (p 2790)
It would be perfectly legitimate to report either risk ratio or rate ratio, or even both, but your choice would depend on your research question and what you were trying to emphasizeThe odds ratio should not be confused with relative risk or hazard ratios which might be close in certain cases, but are completely different measures Odds ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statistics Rate ratio = 10/5 = Rate Ratio vs Risk Ratio What do you report?




Significant Improvement In Short And Long Term Kidney Transplant Survival Despite Stagnant Rates Of Delayed Graft Function Atc Abstracts
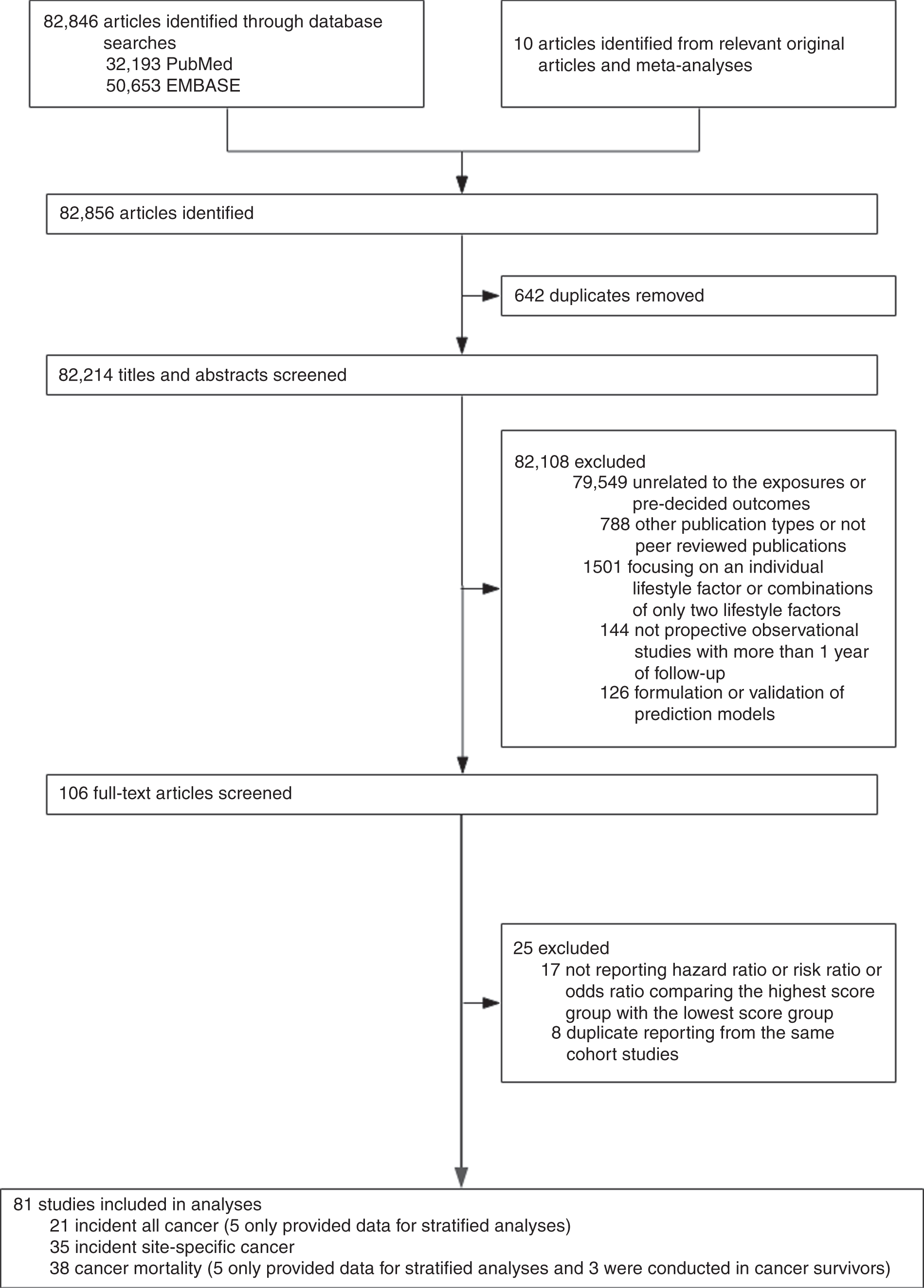



Combined Lifestyle Factors Incident Cancer And Cancer Mortality A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Prospective Cohort Studies British Journal Of Cancer
In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1The method of presenting the results of clinical studies canHazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?
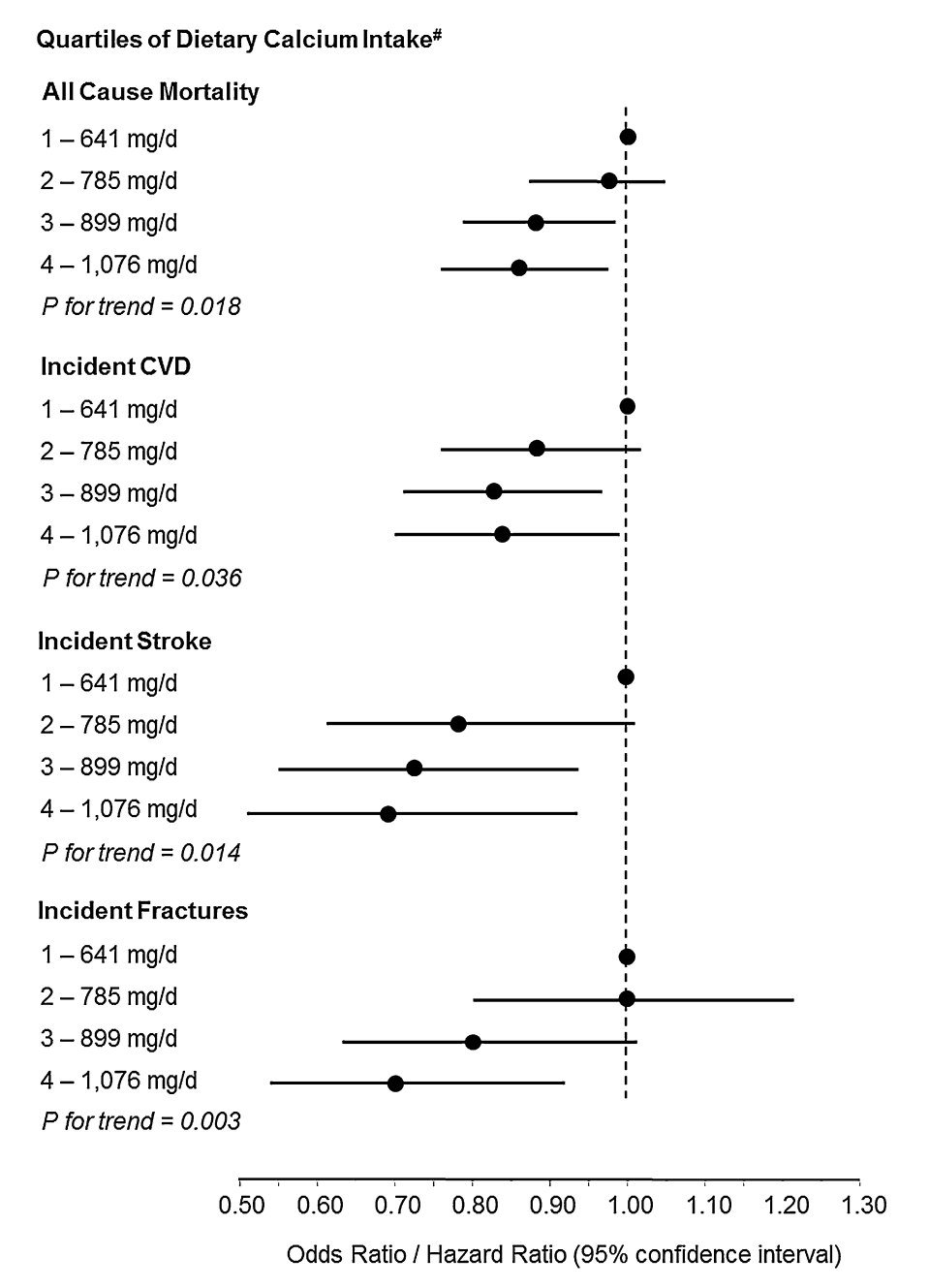



Clanky A Aktuality Clanky A Aktuality 12 18




đo Lư Ng Nh Hư Ng Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Ratio Hazard Ratio
Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the risk ratio Hazard ratios / rate ratios can therefore be constant over the entire range of baseline hazard / background rate Roger Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;



2



Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio
Odds ratio, relative risk, risk ratio, hazard ratio Nguy ễn V ăn Tu ấn Trong bài " Lâm sàng th ống kê 14 ", tôi đã gi ải thích s ự liên h ệ và khác bi ệt gi ữa odds ratio (OR) và relative risk (RR), và nh ững khó kh ăn trong vi ệc di ễn gi ải OR G ần The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4
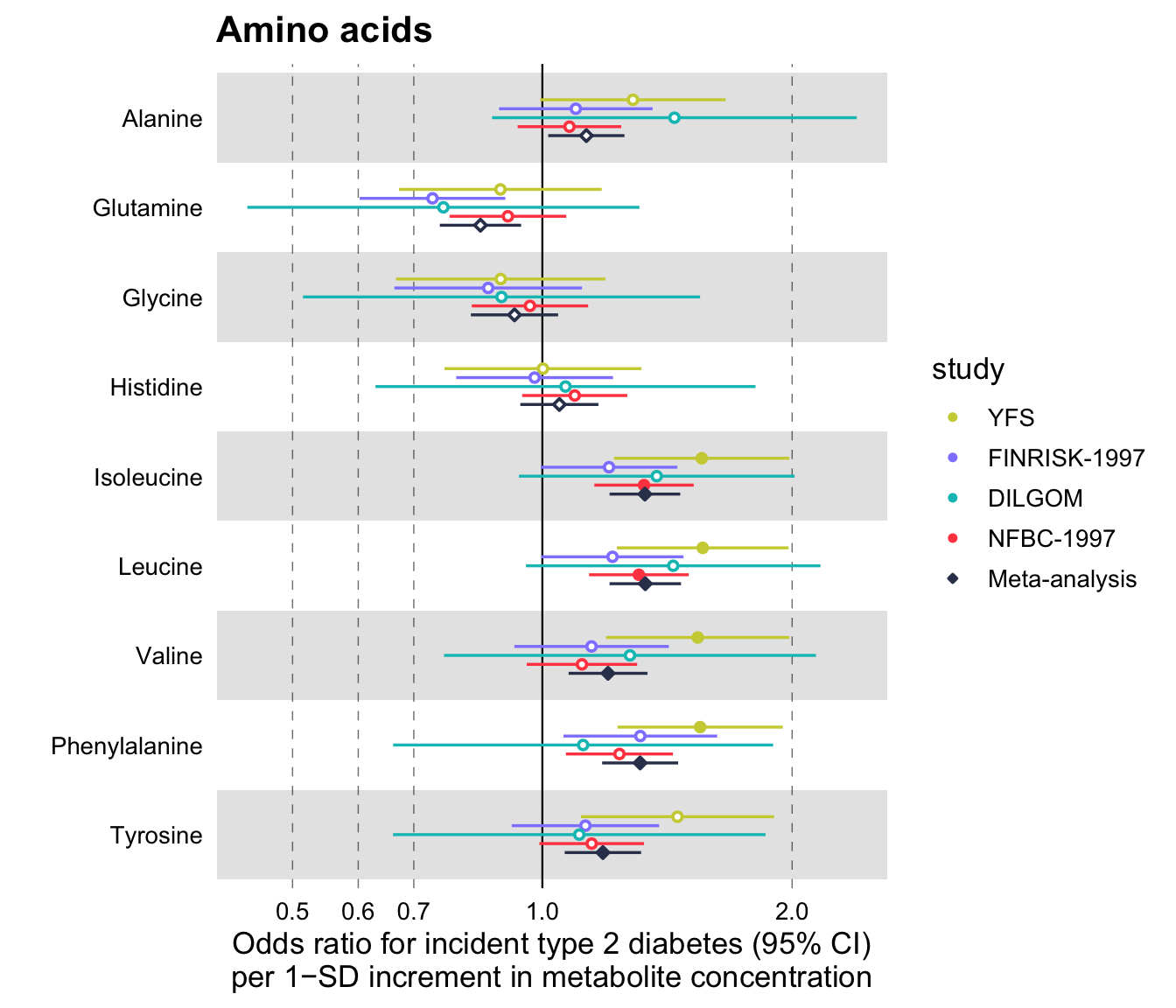



Using Ggforestplot Ggforestplot




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Hazard ratios Hazard ratios are calculated using survival data and survival analysis You would use this if you have a oneoff event as your outcome (for example, death, cancer diagnosis, or discharge from hospital) and follow people up for a variable amount of time Hazard ratio = (hazard rate in intervention group) / (hazard rate in control group)A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios




Inplasy Protocol 1143 Inplasy
Hazard ratio is the ratio of hazards and equals to the hazard rate in the treatment group ÷ the hazard rate in the control group Hazard rate represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event at a particular given point in time after the interventionOdds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data Under proportional hazards it is probably "natural" to thinkVariable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group




Metabolome Subtyping Of Severe Bronchiolitis In Infancy And Risk Of Childhood Asthma Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
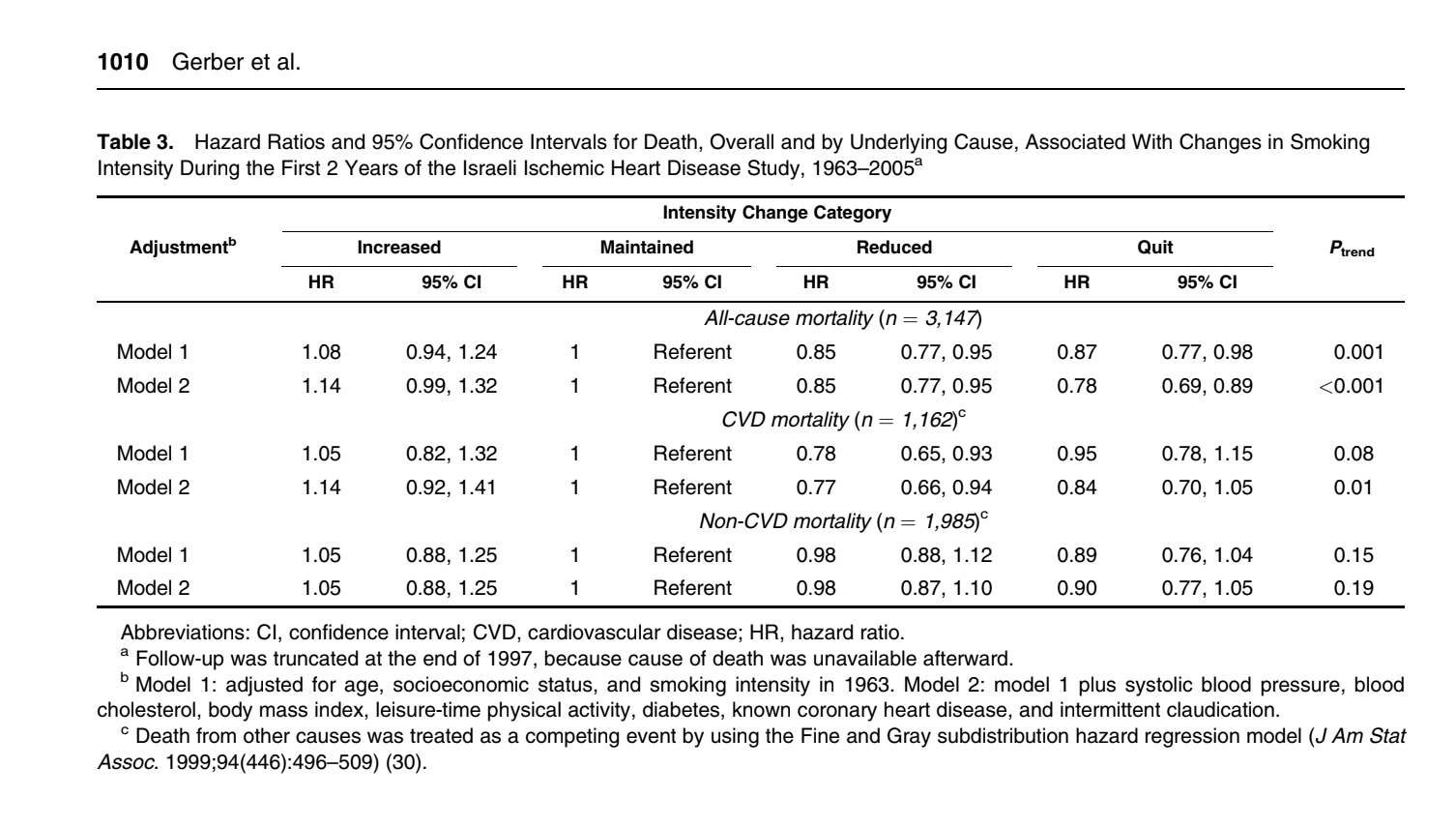



Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com
This video introduces Survival Analysis, and particularly focuses on explaining what the survival functions is, what the hazard is, and what the hazard ratio Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while aRisk, absolute risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio These figures help to determine if the new treatment has an advantage over other treatments or placebo Ways of expressing treatment effects The absolute risk, number needed to treat, relative risk and odds ratio can be calculated by compiling a 2x2 table of study data




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Intervals and statistical vs clinical significance This second article will discuss absolute and relative risks, number needed to treat and harm, KaplanMeier survival curves and understanding diagnostic tests What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/What we model (log) Hazard rate (log) Odds h(t) = lim 4!0 P(t T



Plos One Delirium As A Predictor Of Mortality And Disability Among Hospitalized Patients In Zambia
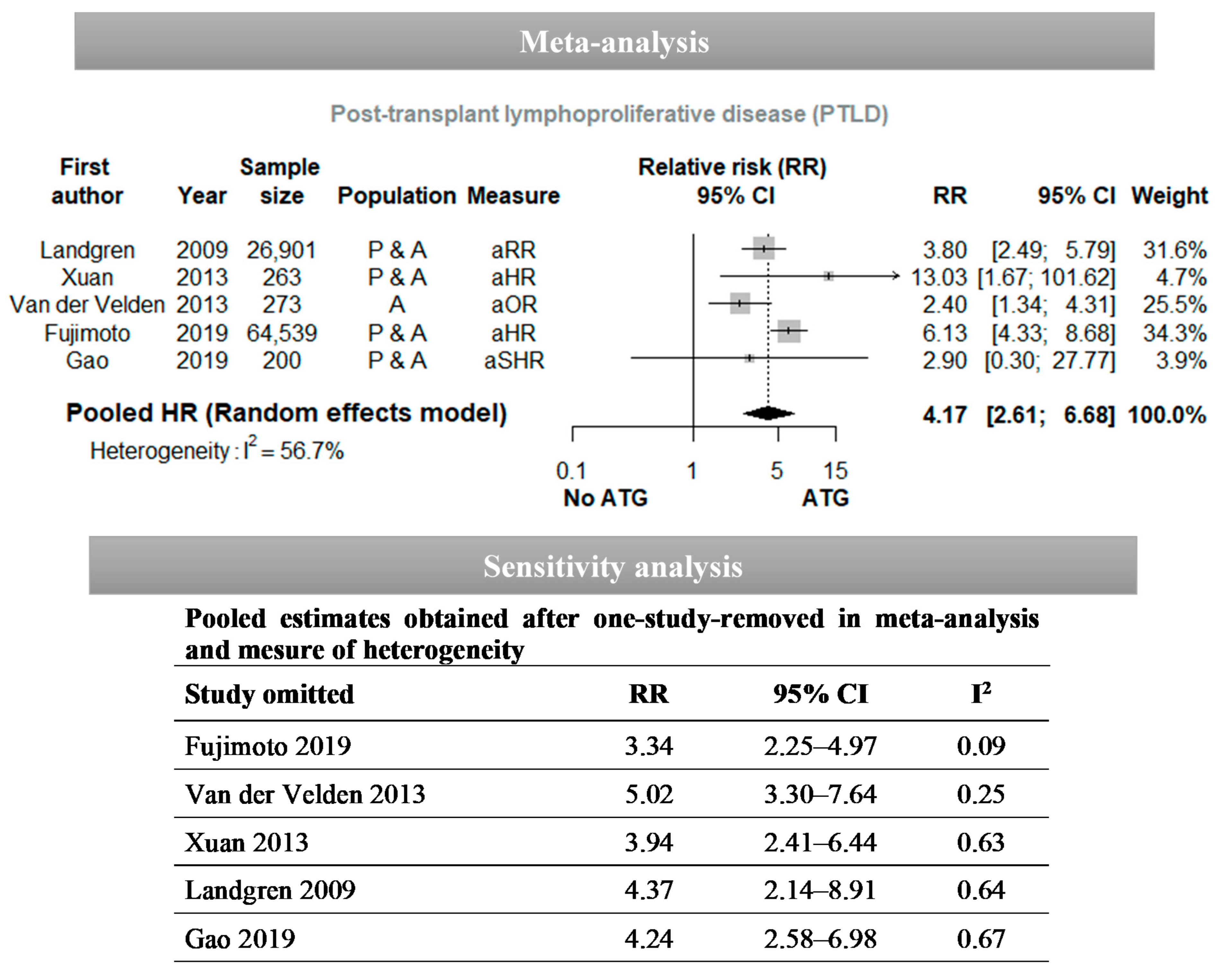



Vaccines Free Full Text Factors Associated With Post Transplant Active Epstein Barr Virus Infection And Lymphoproliferative Disease In Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Html
Furthermore, the odds ratio of 258 for all persons is not a weighted average of the odds ratios of 265 for men and 291 for women, as 258 is closer to 1 than either stratumspecific estimate Adjusting the odds ratio of 258 for sex, using MantelHaenszel methods, produces an odds ratio of 279, though sex is not a confounderThe risk ratio is less than 10, indicating a decreased risk or protective effect for the exposed (vaccinated) children The risk ratio of 028 indicates that vaccinated children were only approximately onefourth as likely (28%, actually) to develop varicella asAn odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, ie, if p 2 equals zero or q



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio
Cependant, dans une étude castémoins, seul l'odds ratio peut être estimé puisque le nombre total de sujets non malades est déterminé par le nombre de témoins choisis par cas Le Hazard Ratio (HR) est proche du RR avec une dimension temporelle supplémentaire Odds ratio is basically the ratio of two odds In this example, OR is ratio of odds that cases were exposed to hormone replacement therapy and odds that controls were exposed to hormone replacement therapy Calculation of odds ratio (OR) There are two things to understand in calculation of odds ratio First we need to understand about oddsAn odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio suggests a strong association



1




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio interpretation Hazard ratio vs odds ratio interpretationAn odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2Cox regression vs logistic regression Distinction between hazard/rate ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precisionRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not




Odds Ratio Versus Hazard Ratio La Estadistica Una Orquesta Hecha Instrumento
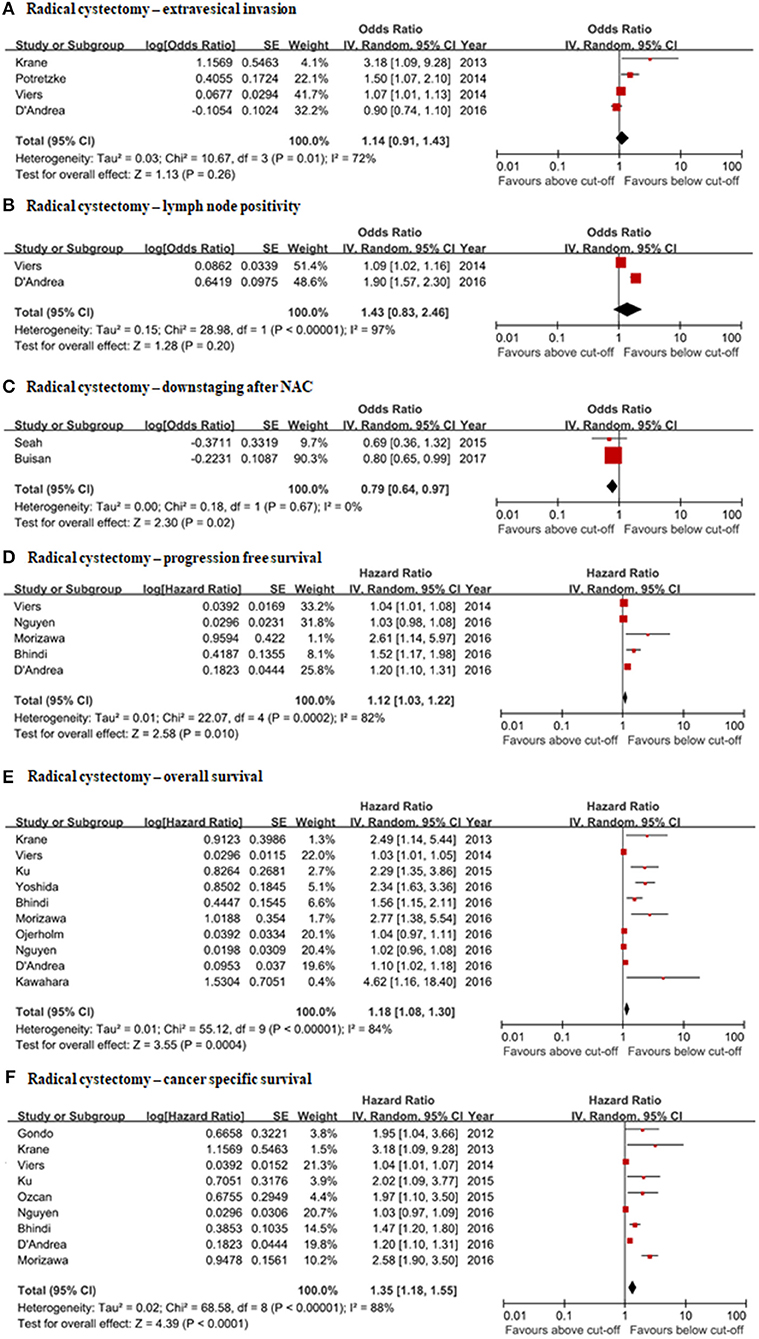



Frontiers Clinical Significance Of Pre Treated Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio In The Management Of Urothelial Carcinoma A Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Oncology
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR Rate ratios are closely related to risk ratios, but they are computed as the ratio of the incidence rate in an exposed group divided by the incidence rate in an unexposed (or less exposed) comparison group Consider an example from The Nurses' Health Study This prospective cohort study was used to investigate the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratio The hazard ratio is derived from calculating the rate (number of events/time) in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratio




Risk Of Pulmonary Embolism And Deep Venous Thrombosis In Patients With Asthma A Nationwide Case Control Study From Sweden European Respiratory Society



Survminer 0 3 0 Easy Guides Wiki Sthda
What is the difference between odds ratio and hazard ratioRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratiosHazard ratio, odds, and probability of healing There is an alternative interpretation of the hazard ratio that may be intuitively easier to understand The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first Thus, in a clinical trial examining time to disease resolution, it Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie diet
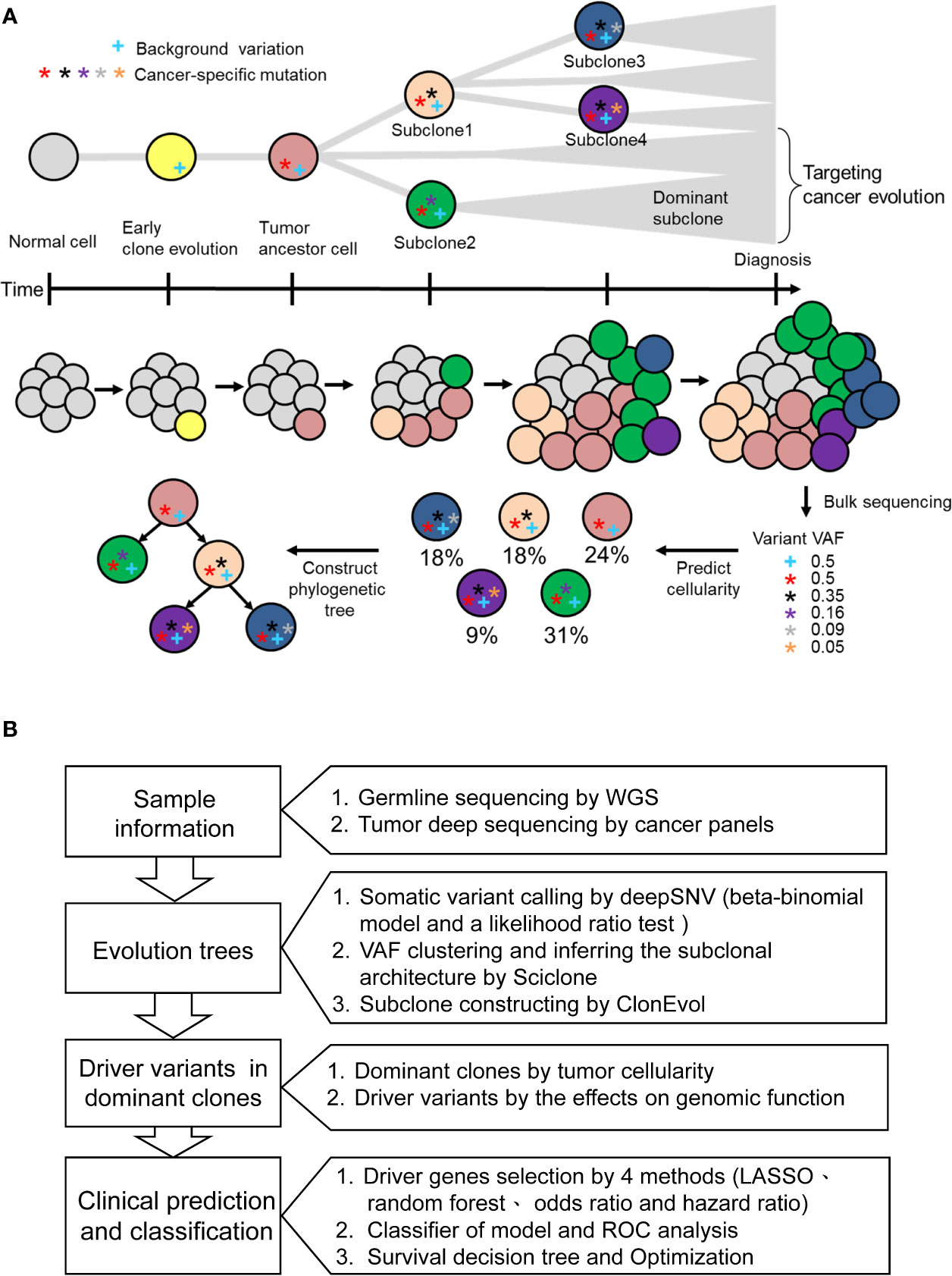



Frontiers Intratumor Heterogeneity Of Myo18a And Fbxw7 Variants Impact The Clinical Outcome Of Stage Iii Colorectal Cancer Oncology




Scielo Brasil Analysis Models For Variables Associated With Breastfeeding Duration Analysis Models For Variables Associated With Breastfeeding Duration




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy
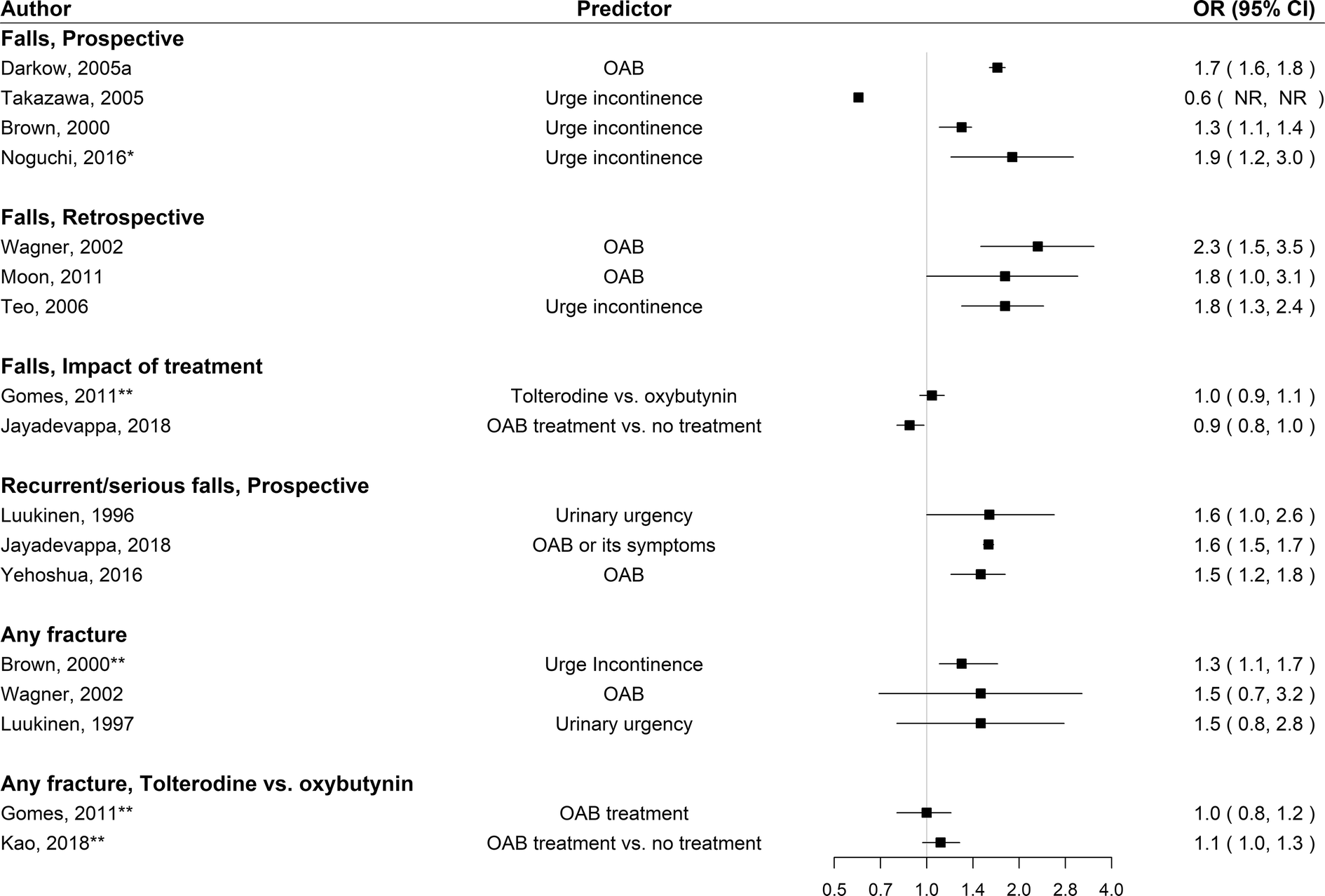



Figure 4 The Association Between Overactive Bladder And Falls And Fractures A Systematic Review Springerlink




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Www Teachepi Org Wp Content Uploads Oldte Documents Courses Fundamentals Pai Lecture4 Measures of effect and impact Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau



Forest Plot Showing The Pooled Odds Ratio Or Or Hazard Ratio Hr Of Download Scientific Diagram




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv




Figure 1 A Forest Plot Of Common Odds Ratios Adjusted For Ecog Ps For Best Overall Response By A Priori Subgroups In Patients With Kras Wild Type Ppt Download




Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Www Mdpi Com 1660 4601 17 24 9336 Pdf




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
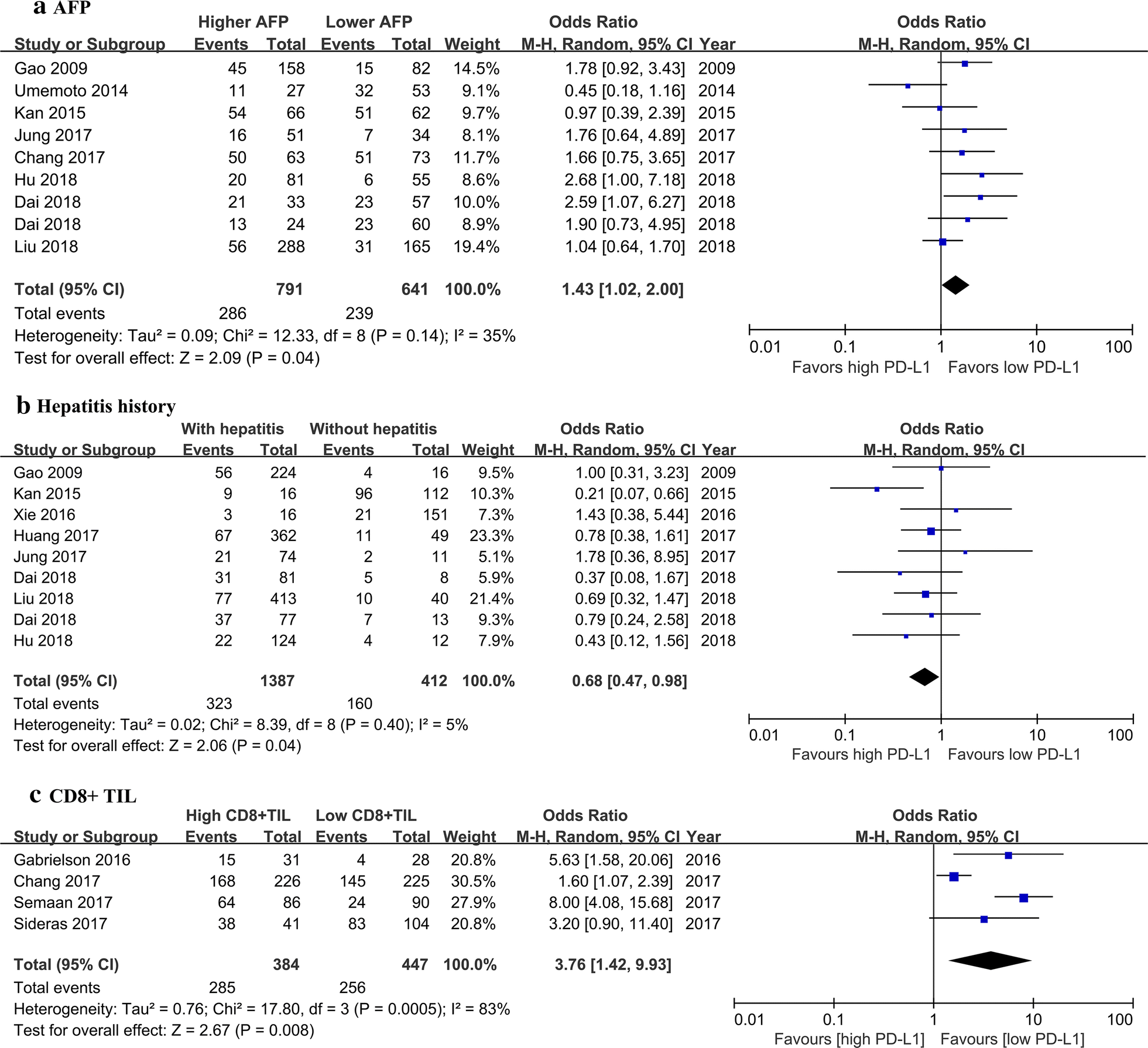



Prognostic Role Of Pd L1 For Hcc Patients After Potentially Curative Resection A Meta Analysis Cancer Cell International Full Text




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Delta Method Standard Errors




Pdf Analysis Of Odds Probability And Hazard Ratios From 2 By 2 Tables To Two Sample Survival Data Semantic Scholar
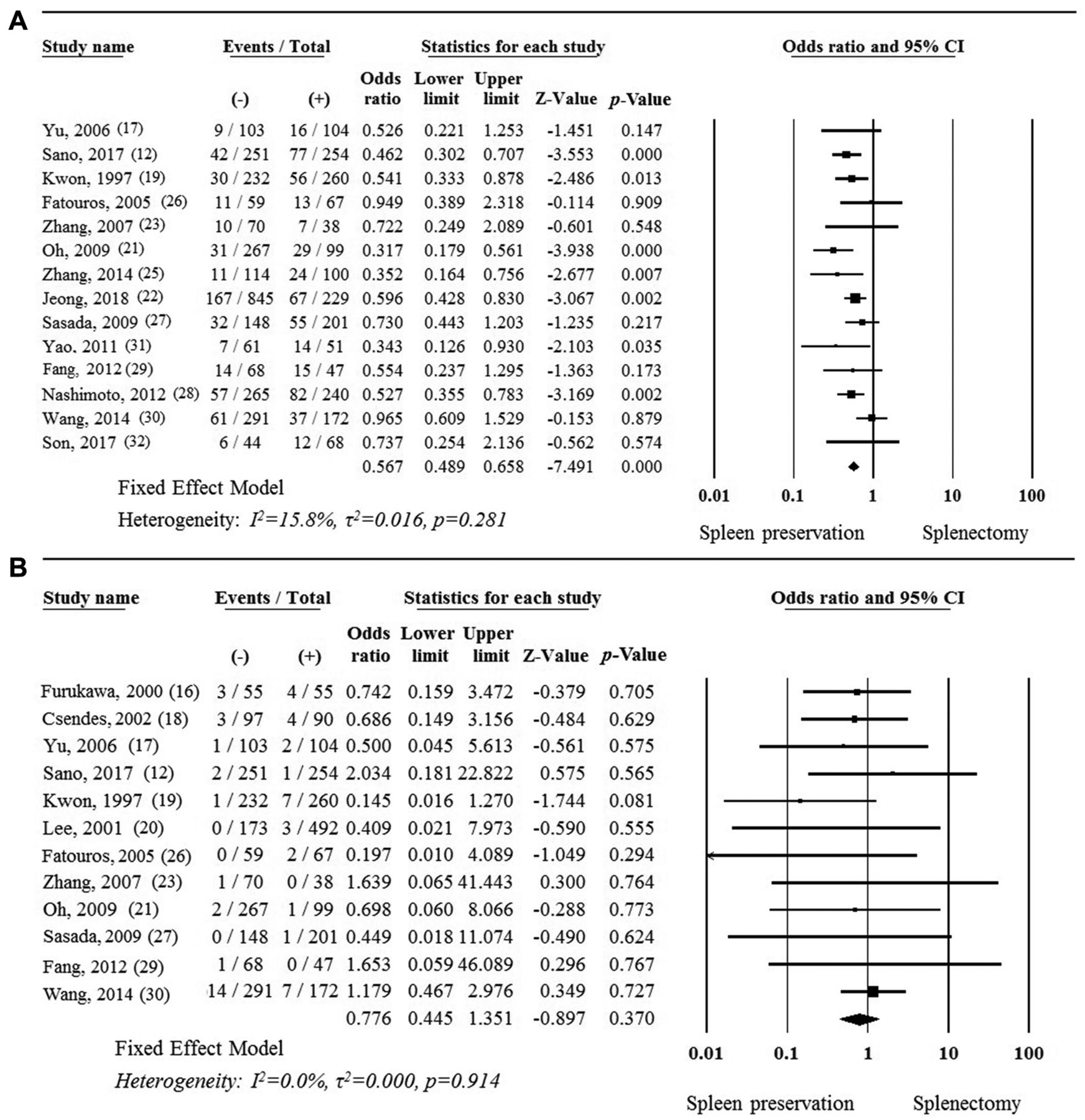



Systemic Review And Meta Analysis Of Impact Of Splenectomy For Advanced Gastric Cancer In Vivo




Association Of Bisphenol A With Puberty Timing A Meta Analysis



Drmeta




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Http Aspirekpco Weebly Com Uploads 1 5 9 3 Session 6 Statistical Interpretation 19 Pdf




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet



Phdres Caregate Net Conferences Ay 13 14 ppt presentations Statistics 102 Pdf




Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population




Linear Combinations Of Estimators Logistic Regression Coefficient Of Determination




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




Long Term Risk Of Dementia Following Hospitalization Due To Physical Diseases A Multicohort Study Sipila Alzheimer S Amp Dementia Wiley Online Library
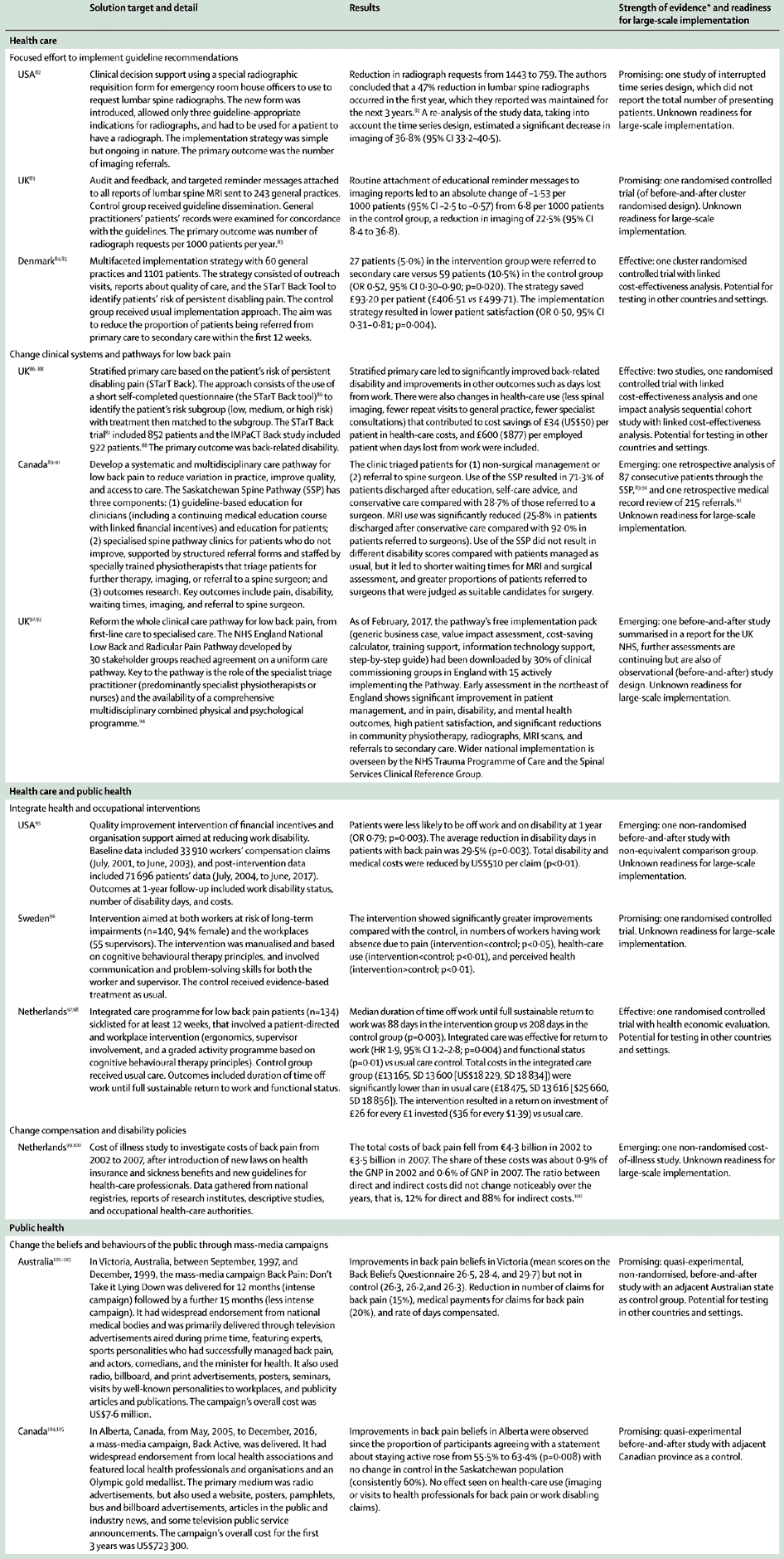



Table 3 Examples Of Effective Promising Or Emerging Solutions By Solution Target




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Www Goldjournal Net Article S0090 4295 18 8 Pdf




Meta Analysis Of Vitamin D Sufficiency For Improving Survival Of Patients With Breast Cancer Anticancer Research



2



Www Cebm Ox Ac Uk Files Data Extraction Tips Blog 10 Pdf
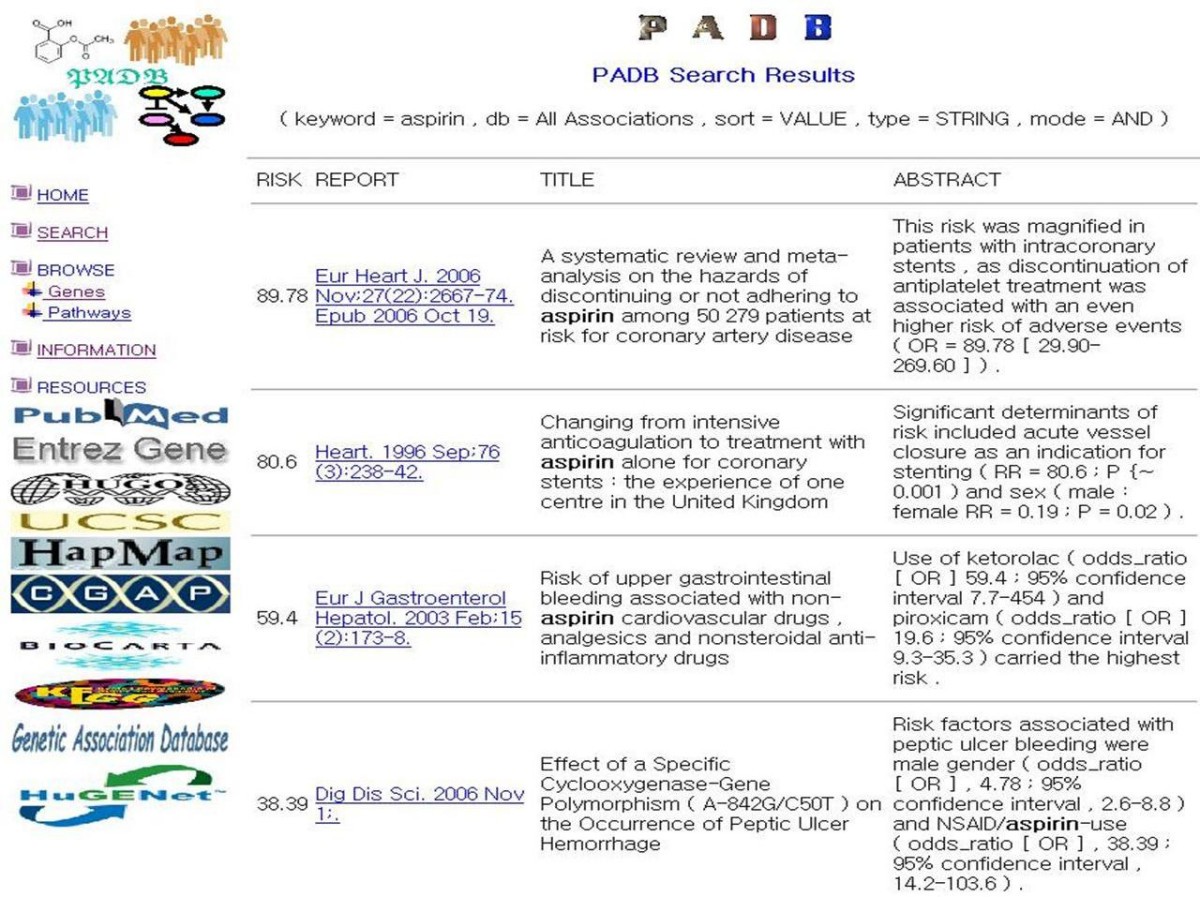



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text



Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort




Journal Of Stroke
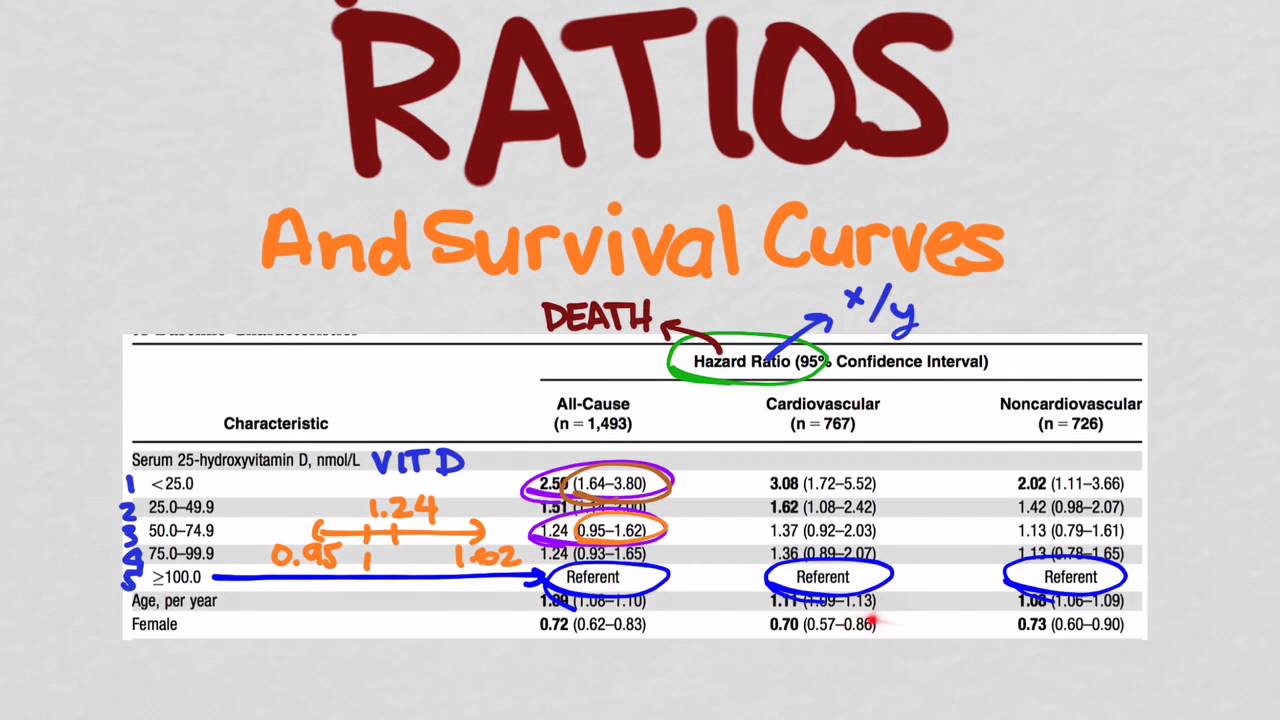



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Support Sas Com Resources Papers Proceedings15 3419 15 Pdf




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
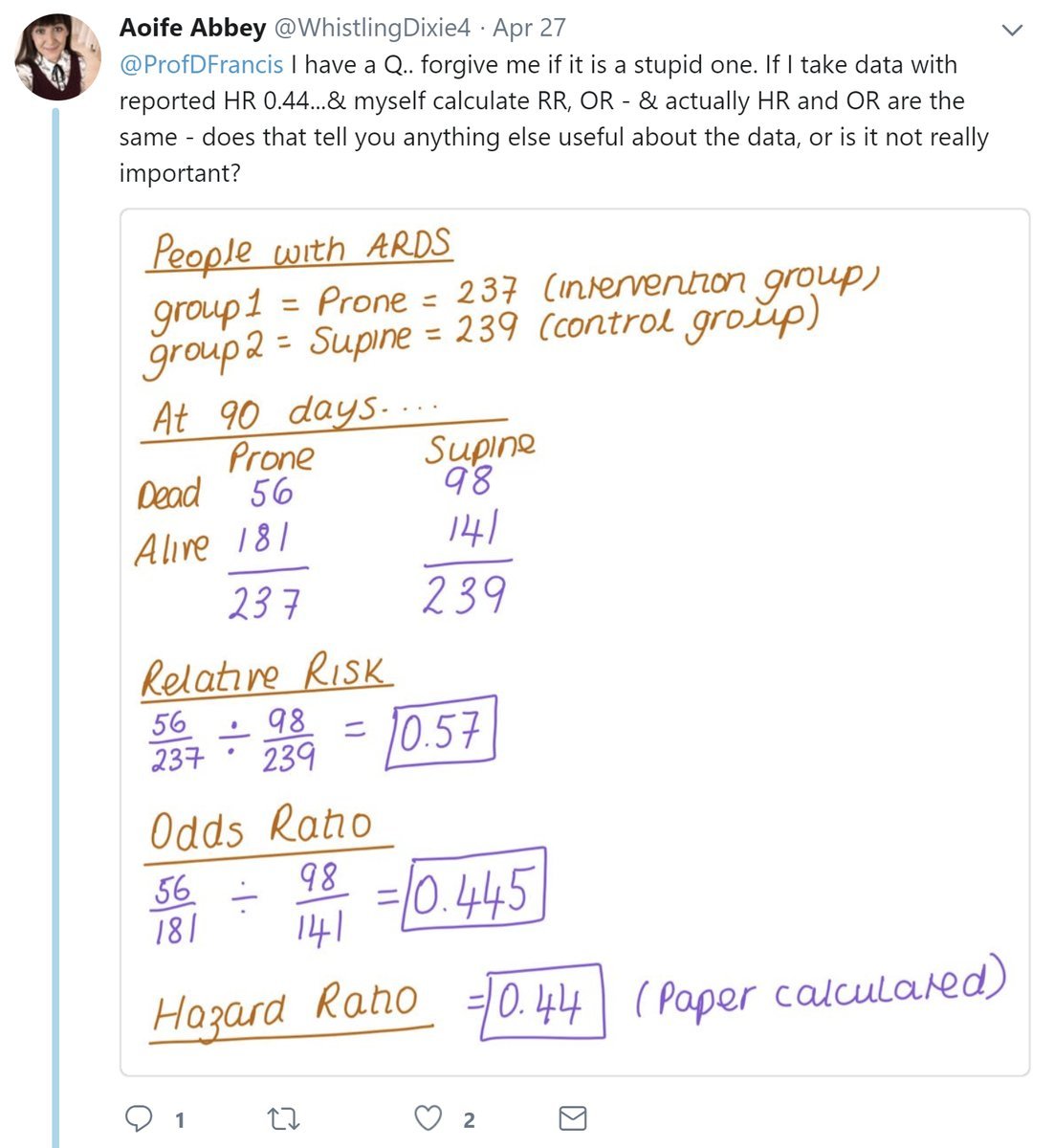



Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And



2




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv



1




Relative Risk Wikipedia
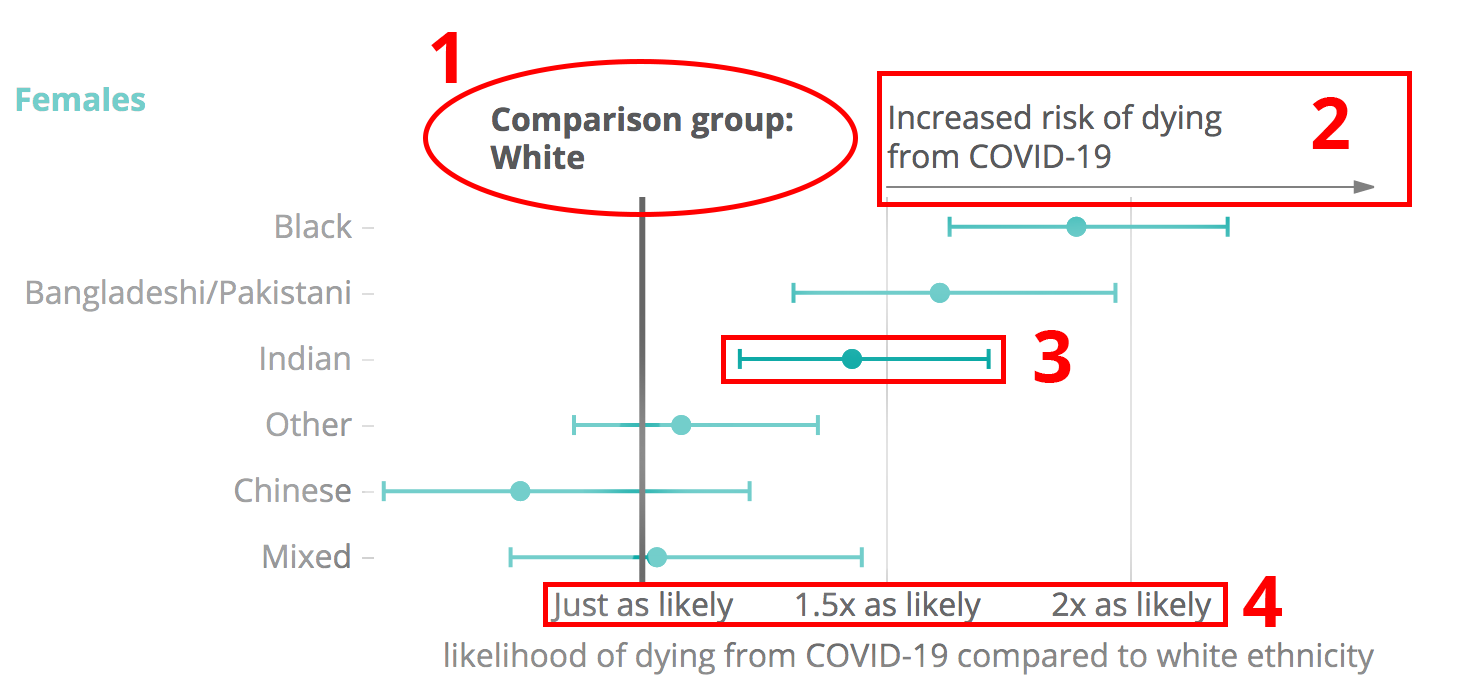



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
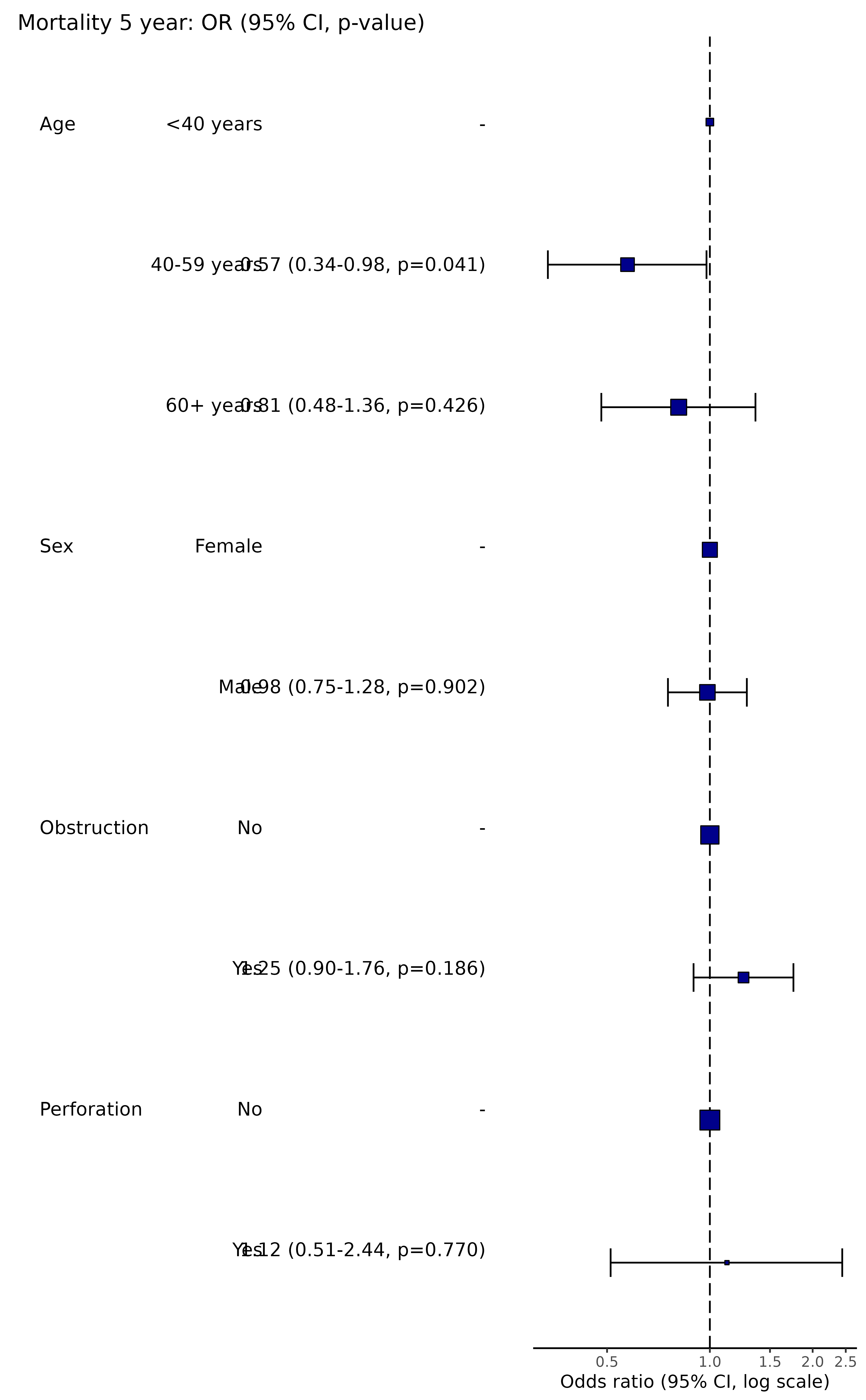



Produce A Table And Plot Ff Plot Finalfit




Forest Plot Of Odds Ratio Or And 95 Confidence Interval Ci For Each Study Of The Association Between The 1131t C Polymorphism And Metabolic Syndrome Risk Under Dominant Model Carriers Vs Non Carriers In



Arxiv Org Pdf 2105




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
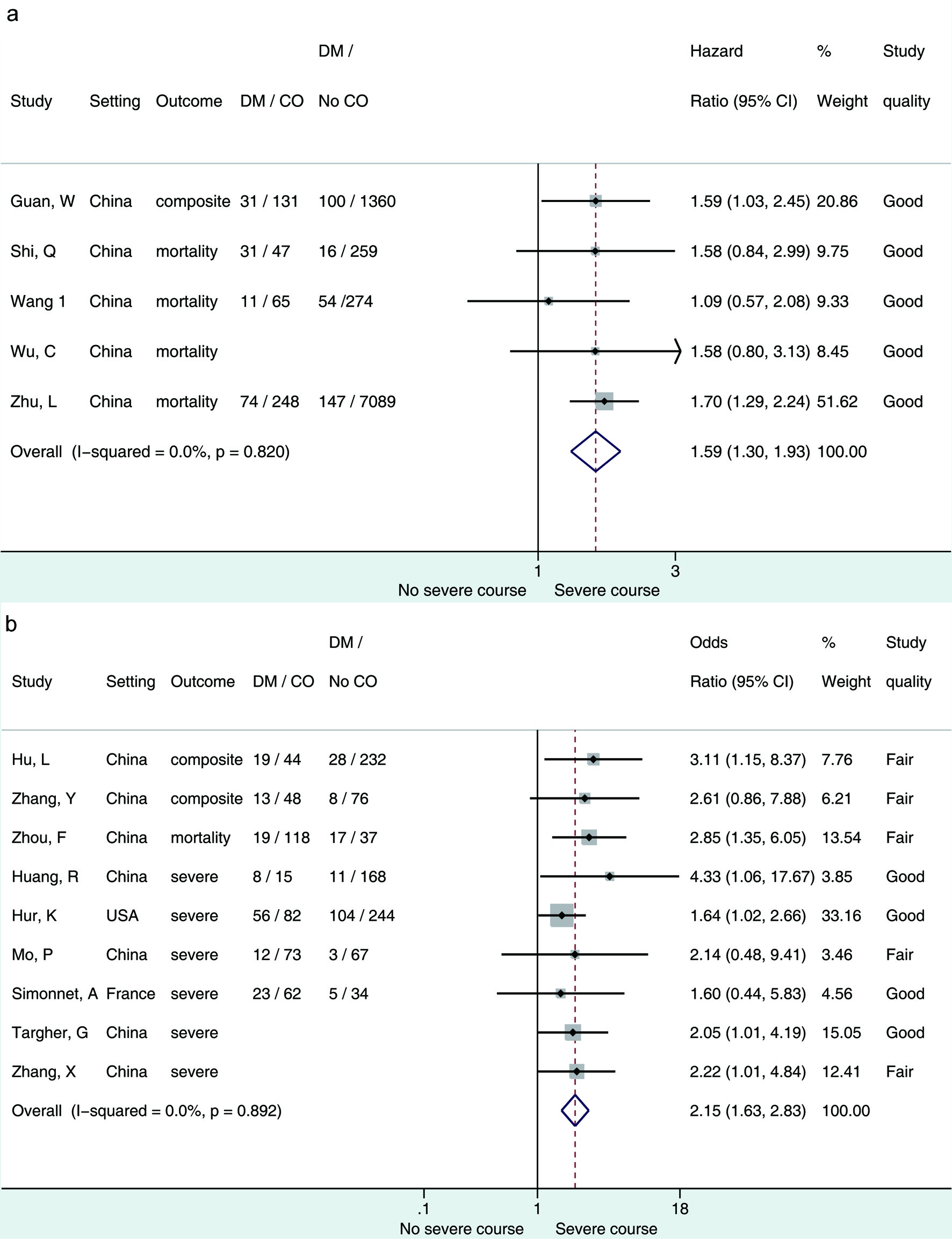



J Endocrinol Metab




Assisted Ventilation In Copd Association Between Previous Hosp Copd




Biostatisticssummarypage



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Www Lexjansen Com Phuse 18 Dv Dv04 Pdf
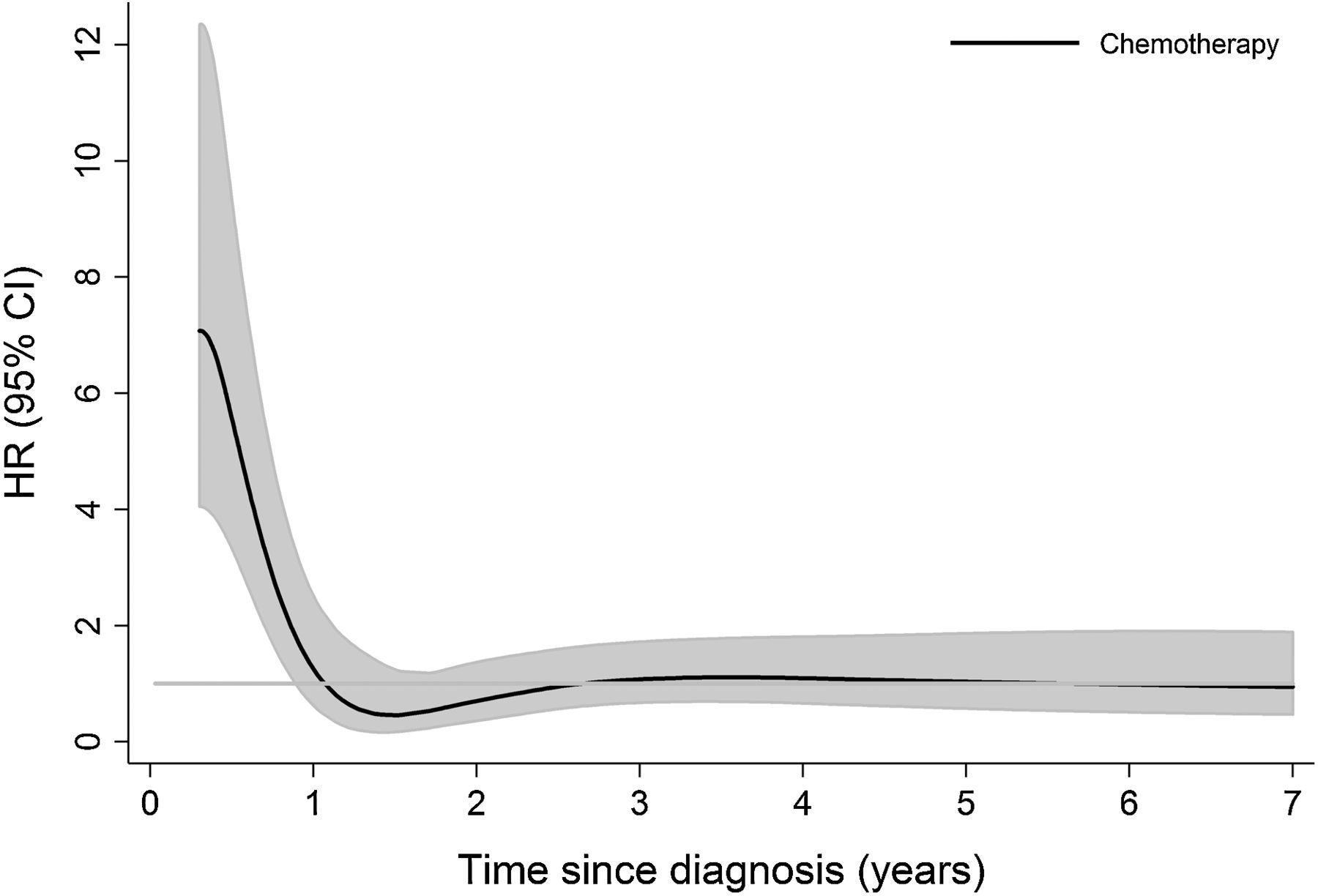



Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum




The Effects Of Diabetes On The Risks Of Major Cardiovascular Diseases And Death In The Asia Pacific Region Diabetes Care
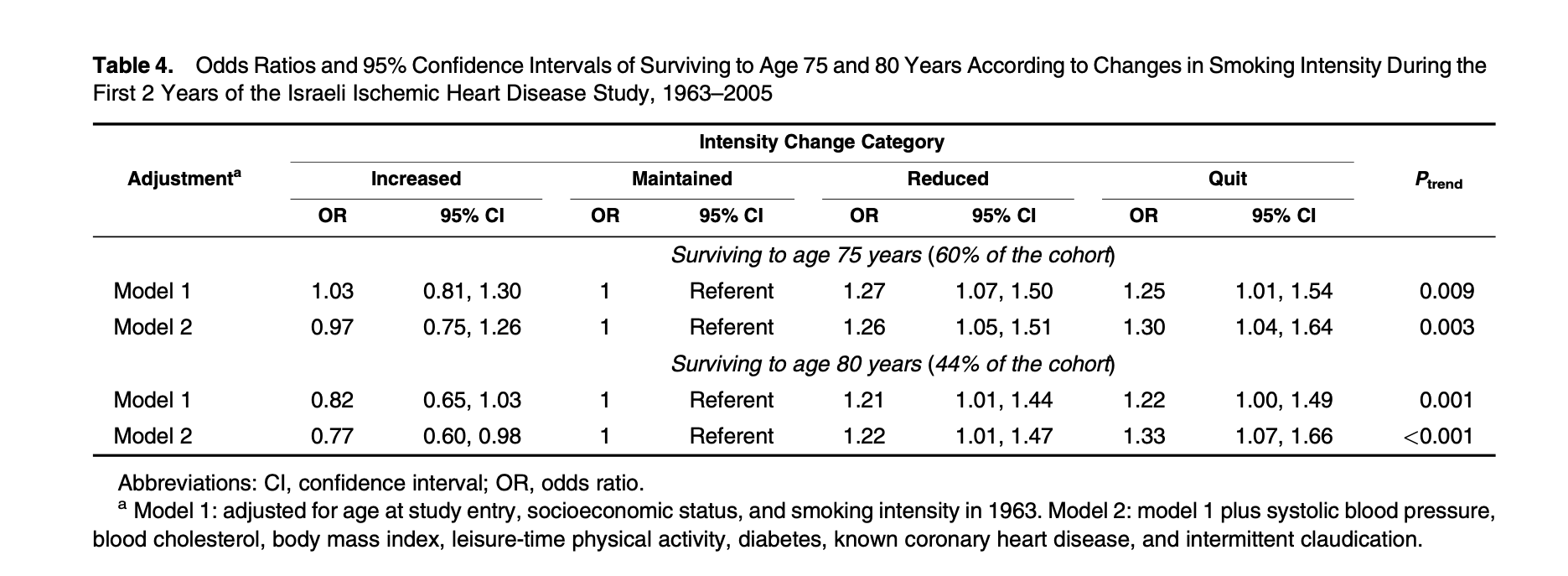



Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com
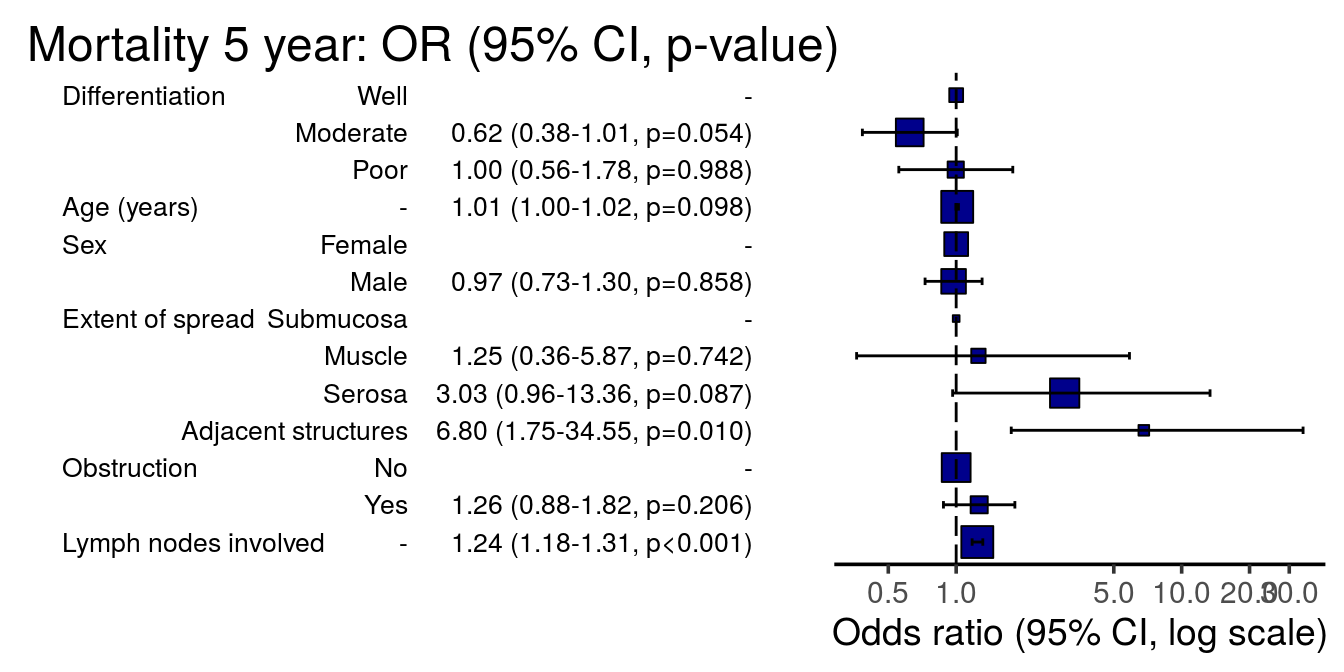



13 5 Odds Ratio Plot R For Health Data Science



Http Journal Emwa Org Observational Studies Odd Cases And Risky Cohorts Measures Of Risk And Association In Observational Studies Article 3240 Mew 263 Lang Pdf




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Iresearch Sa Home Facebook




Functional Promoter Variant In Zinc Finger Protein 2 Predicts Severe Atherosclerosis And Ischemic Heart Disease Sciencedirect




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True



Www Jstor Org Stable
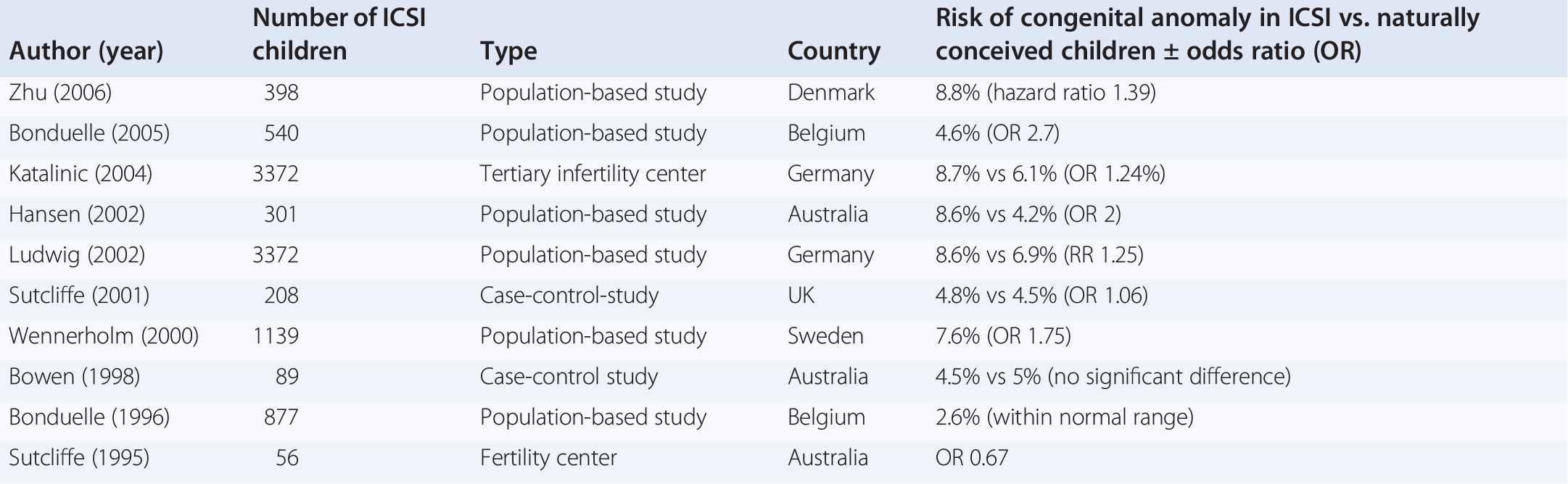



Congenital Anomalies And Assisted Reproductive Technologies Chapter 34 Ultrasonography In Reproductive Medicine And Infertility
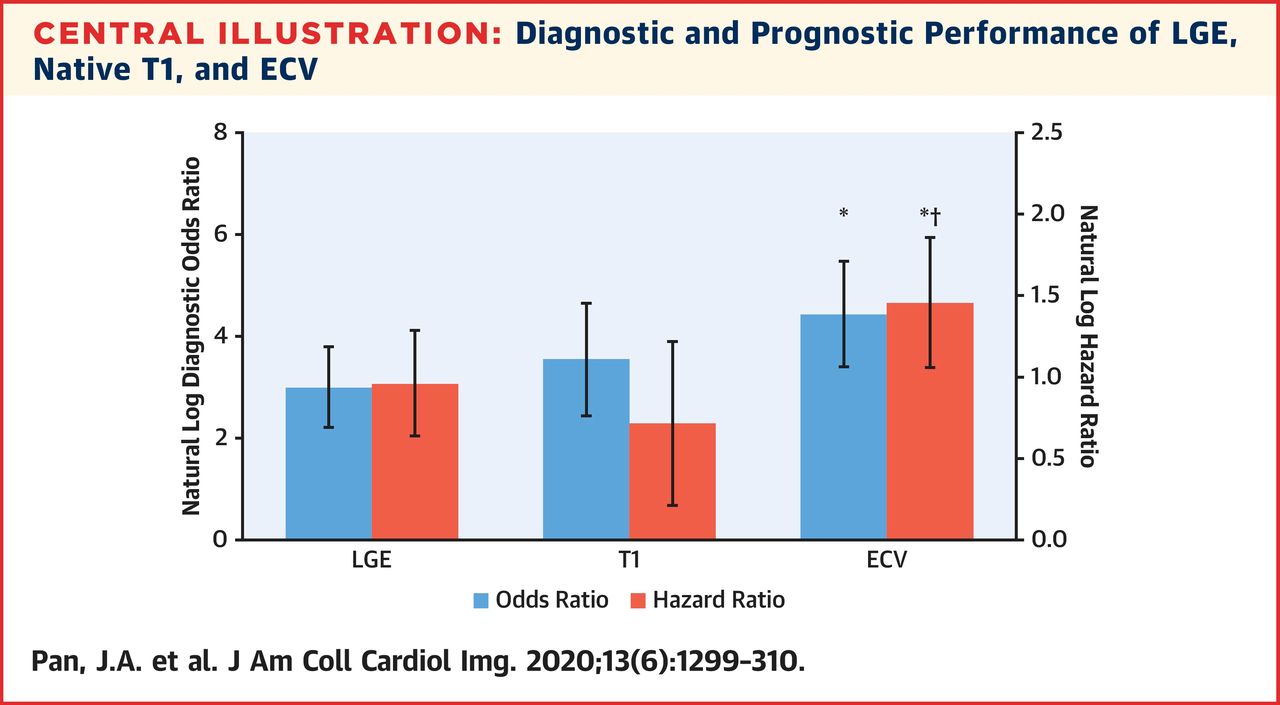



Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Psb 62



2




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿