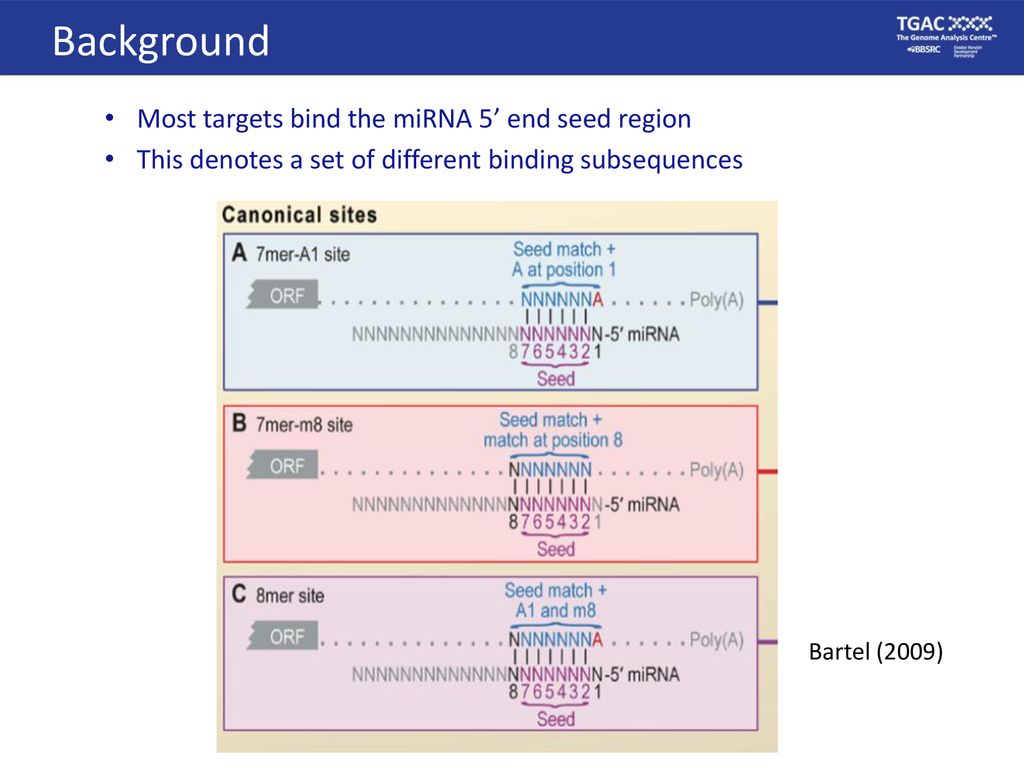
miRNA SniPer An online tool for the detection of miRNA polymorphisms in vertebrates miRNA SNiPer accepts a list of miRNA genes and returns a table of variations within different regions of miRNA genes premiRNA, mature, seed region human; The stability between seed region and target mRNA is a determinant of the efficacy of siRNA offtarget effects 33 Thus, the high stability ofTargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA As an option, only conserved sites are predicted Also identified are sites with mismatches in the seed region that are compensated by conserved 3' pairing and centered sites In mammals, predictions are ranked based on the
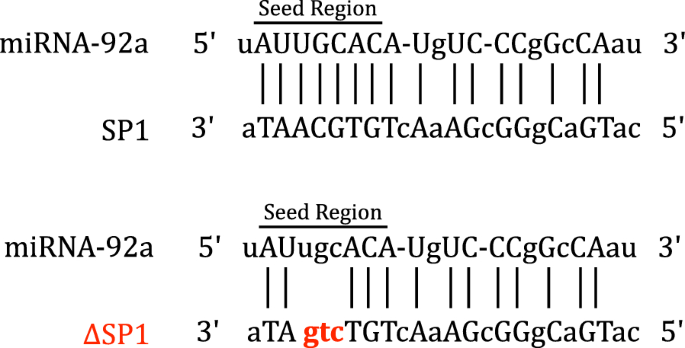
Microrna 92a Regulates The Expression Of Aphid Bacteriocyte Specific Secreted Protein 1 Bmc Research Notes Full Text
Seed region of each mirna
Seed region of each mirna- It is thought that most miRNAmRNA interactions involve the seed region at the 5′ end of the miRNA The importance of seed sites is supported by experimental evidence, although there is growing interest in interactions mediated by the central region of the miRNA, termed centered sites To investigate the prevalence of these interactions, we apply a biotin pulldown method toSingle nucleotide substitution in the seed region of miR96 induces a significant discordance in promyleocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) transcript targeting To our knowledge, the SNP (rs) in miR96 is the first confirmed example of a novel target binding site being created by a SNP within a miRNA seed sequenceOtherwise reject R (0) i (3) For each region, find all points that



Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html
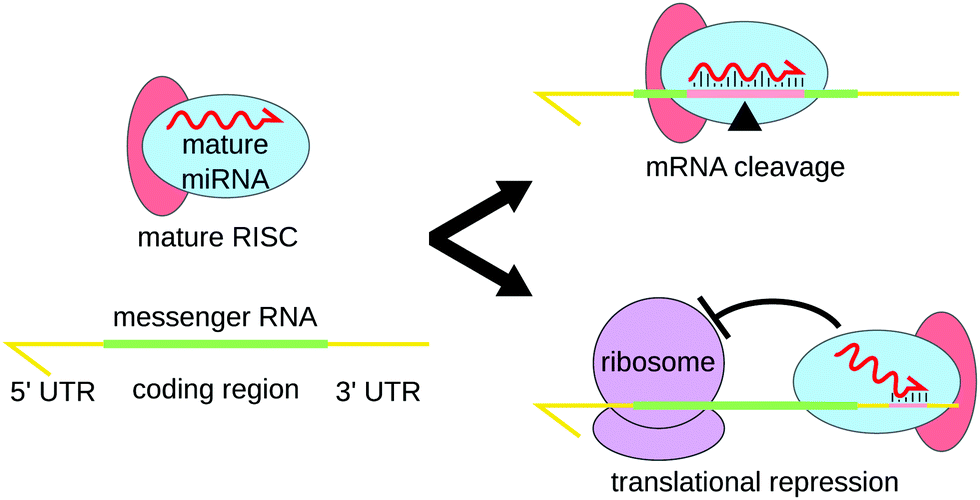
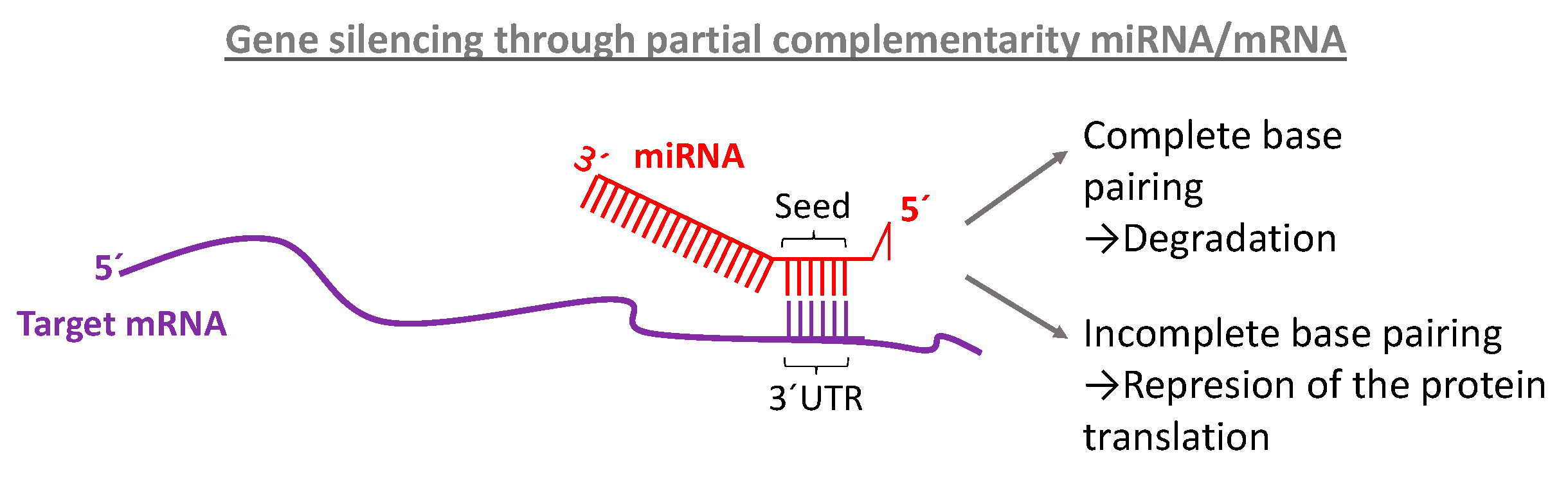
Canonically, miRNA targeting is reliant on base pairing of the seed region, nucleotides 2–7, of the miRNA to sites in mRNA 3′ untranslated regions Recently, the 3′ half of the miRNA has gained attention for newly appreciated roles in regulating target specificity and regulation In addition, the extent of pairing to the miRNA 3′ endSeed region of mirna Seed region of mirnaA mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing to the 3′ region of the miRNA was not critical for silencingThe seed sequence or seed region is aPasquinelli, 12) In contrast, most evidence indicates that miRNAs in land plants require more extensive pairing to their targets (Schwab et al, 05;
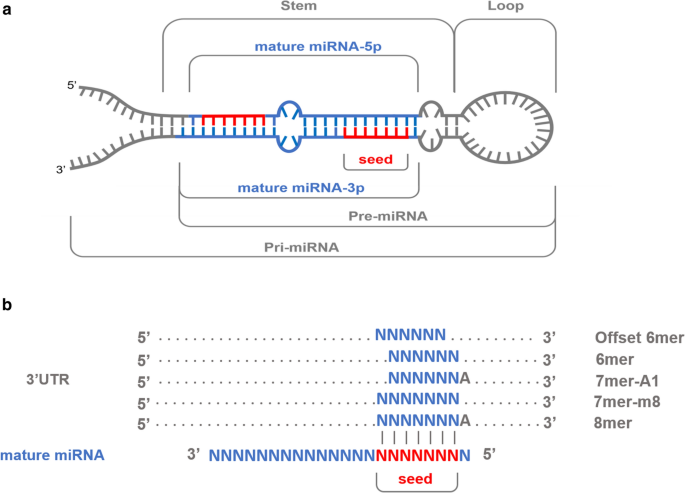
Moreover, the requirement of a 7nt match to the seed region of the miRNA (nucleotides 2–8) could be relaxed to require a 6nt match to a reduced seed comprising nucleotides 2–7 of the miRNA while still retaining modest specificity Running TargetScan in this way without cutoffs amounted to predicting a target simply by virtue of the presence of at leastOther animals (selectable) plants (selectable) miRNA basic informationThe seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary
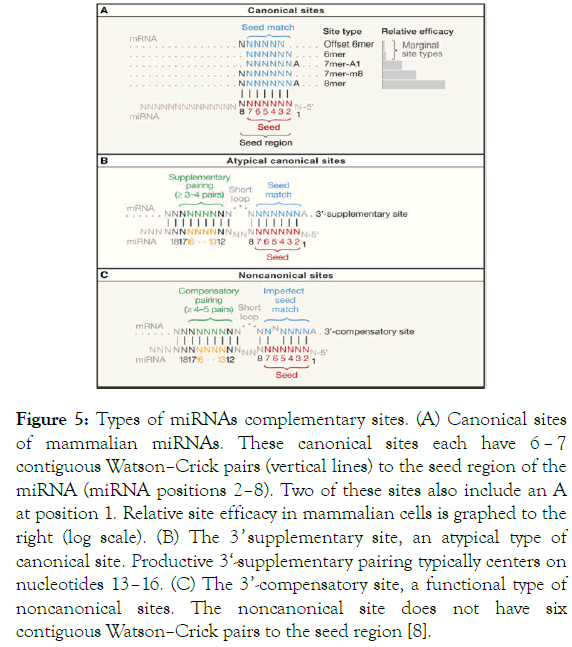
MiRNA seed region is more critical than the 3′ region for target recognition in A thaliana (Mallory et al, 04) Moreover, plant and algal small RNAs also induce translational repression of perfectly complementary target mRNAs without, or with only minimal, transcript destabilization, thereby adding to the mechanistic complexity of miRNA action (Brodersen et al, 08;In human miRNA seed regions and explore the clustering Clustered miRNAs with SNPs in the seed region Nonclustered miRNAs with SNPs in the seed region 0 10 30 40 50 Percent overlap (%) ⁎ Figure 2 Difference in the functional effect of SNPs in clustered and nonclustered miRNA seed regions ∗P Target recognition occurs primarily through the miRNA seed region, composed of guide (g) nucleotides g2–g8 However, nucleotides beyond the seed are also important for some known miRNA–target interactions Here, we report the structure of human Argonaute2 (Ago2) engaged with a target RNA recognized through both miRNA seed and supplementary (g13–g16)




Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html




Different Mirna Mrna Seed Site Interaction Patterns 6mer 7mer A1 Download Scientific Diagram
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous small noncoding RNAs that participate in a majority of biological processes via regulating target gene expression The posttranscriptional repression through miRNA seed region binding to 3′ UTR of target mRNA is considered as the canonical mode of miRNAmediated gene regulation However, emerging evidence suggests that MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulators of gene expression that control various biological processes The role of many identified miRNAs is not yet resolved Recent evidence suggests that miRNA mutations and/or misexpression may contribute to genetic disorders Point mutations in the seed region of MIR184 have been recently identified in Keratoconus (KC) patients with orOnline GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis Bahar Yilmazel1, Yanhui Hu1, Frederic Sigoillot2, Jennifer A Smith3, Caroline E Shamu3, Norbert Perrimon1,4 and Stephanie E Mohr1* Abstract Background RNA interference (RNAi) is an effective and important tool used to study gene function For largescale screens,




Mirna Therapeutics A New Class Of Drugs With Potential Therapeutic Applications In The Heart Future Medicinal Chemistry




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell
Predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of sites that match the seed region of each miRNA In flies and nematodes, predictions are ranked based on the probability of their evolutionary conservation In zebrafish, predictions are ranked based on site number, site type, and site context, which includes factors that influence targetsite accessibility In mammals, the SiRNA is designed to be perfectly complementary to the target mRNA and, miRNA follows the "seedpairing rule", a complementary binding of miRNA seed region to binding site (BS) located in the mRNA 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) (Figure (Figure1C) 1 C) The seed region involves nt 28 from miRNA 5' end or possibly nt 27 and 26Mouse miRNA basic information;




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect




Mirna Seed Types Nine Seed Types Are Categorized In Two Groups Download Scientific Diagram
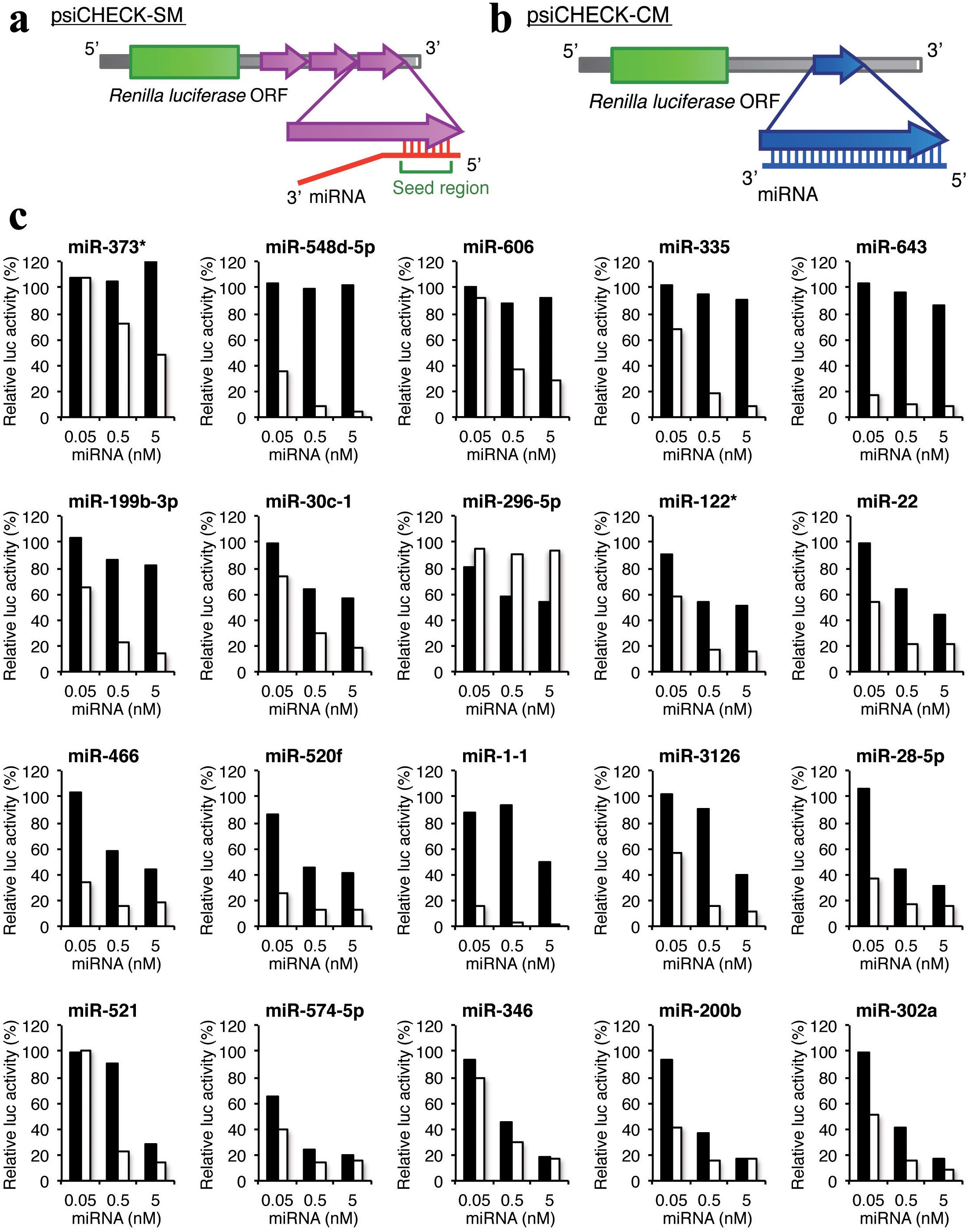
The human genome encodes over 1000 miRNA genes that collectively target the vast majority of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) Basepairing of the socalled miRNA "seed" region with mRNAs identifies many thousands of putative targets Evaluating the strength of the resulting mRNA repression remains challenging, but is essential for a biologically informative ranking of potential The list of putative targets perfectly matching the miRNA seed region (positions 2–8) was intersected with a list of experimentally validated miRNA targets Genes present on both lists were placed in the 'Validated Targets' group, while genes predicted to interact with miRNA but which have not been experimentally confirmed, were placed in 'Remaining Genes' group The GC Seed region Seed region of mirna リンクを取得 ;
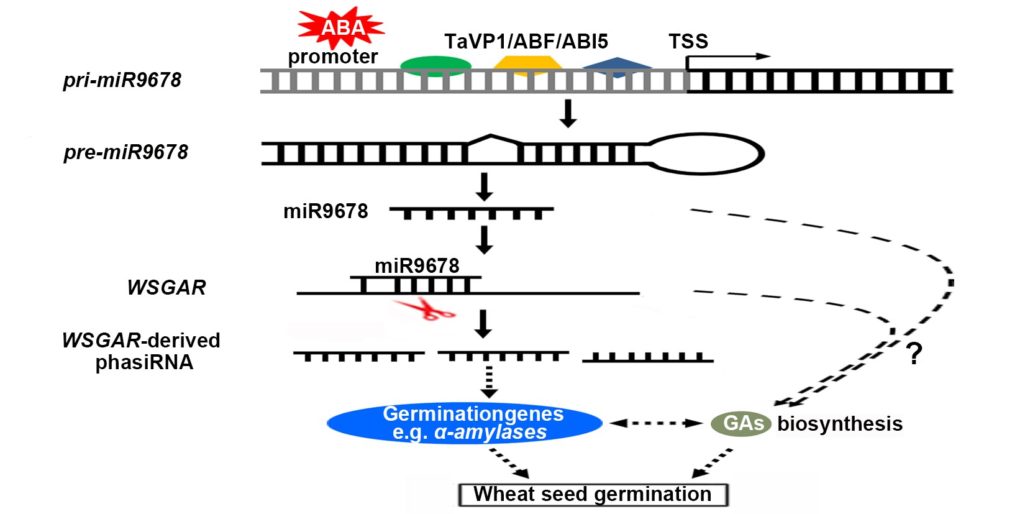



Plantae Mirna Mediated Regulation Of Germination Plantae
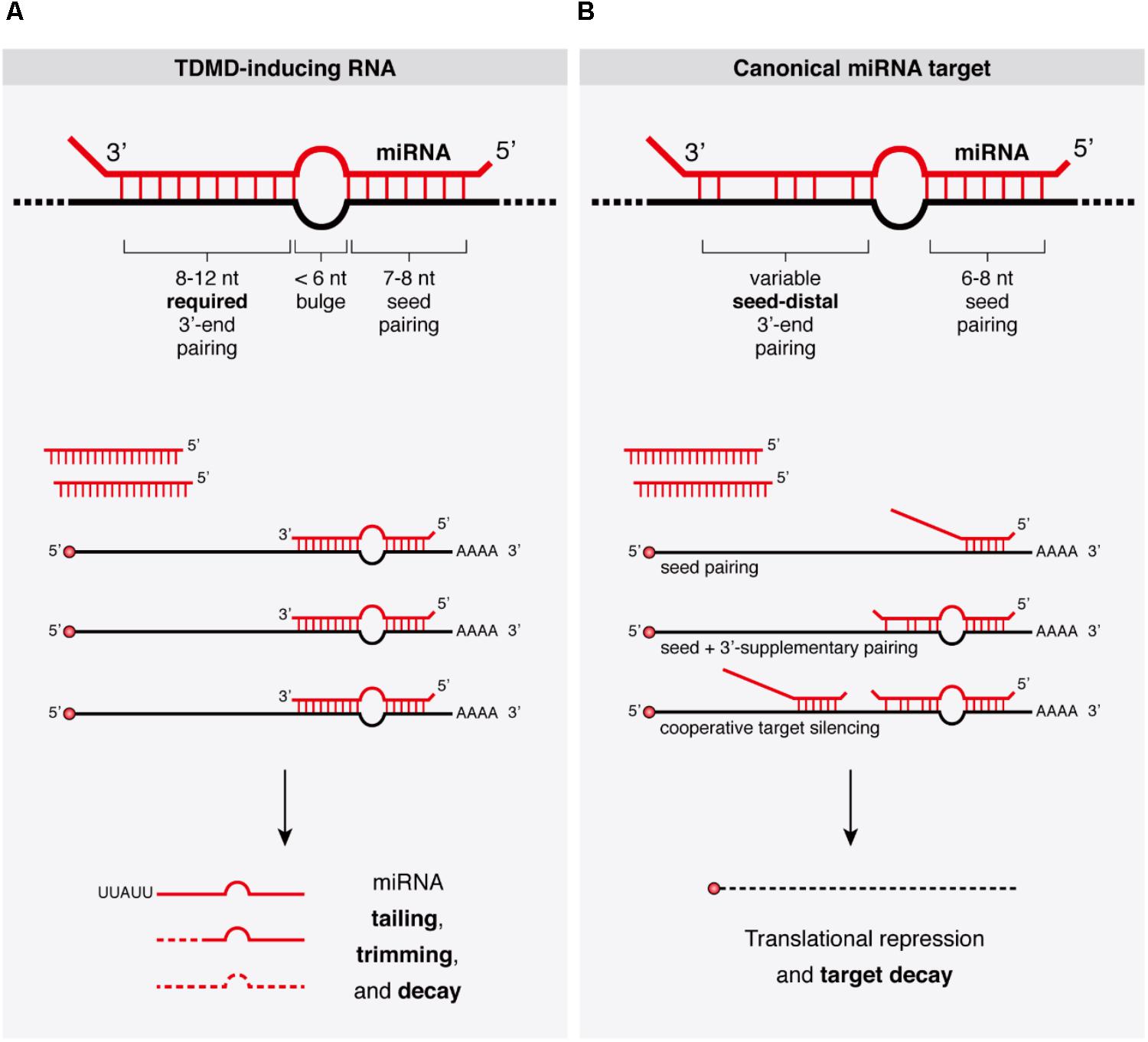



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics
The seed regions are regions present within the miRNA binding regions Although there are several factors that pave a way to the binding between miRNA and mRNA, the impact of binding is determined by the seed sequence within the miRNA The seed region consists of a continuous string of at least 6 to 8 nucleotides miRNA recognizes its target byKim, Heo and Kim, 10;Different miRNAmRNA seedsite interaction patterns (6mer, 7merA1, 7merm8 and 8mer) WatsonCrick complimentary regions can be obtained at miRNA seed and outseed part Base pairing of the miRNA seed region (positions 2–8 from the 5′ end of an miRNA) in animals is critical for target recognition and repression (Bartel, 09;




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science
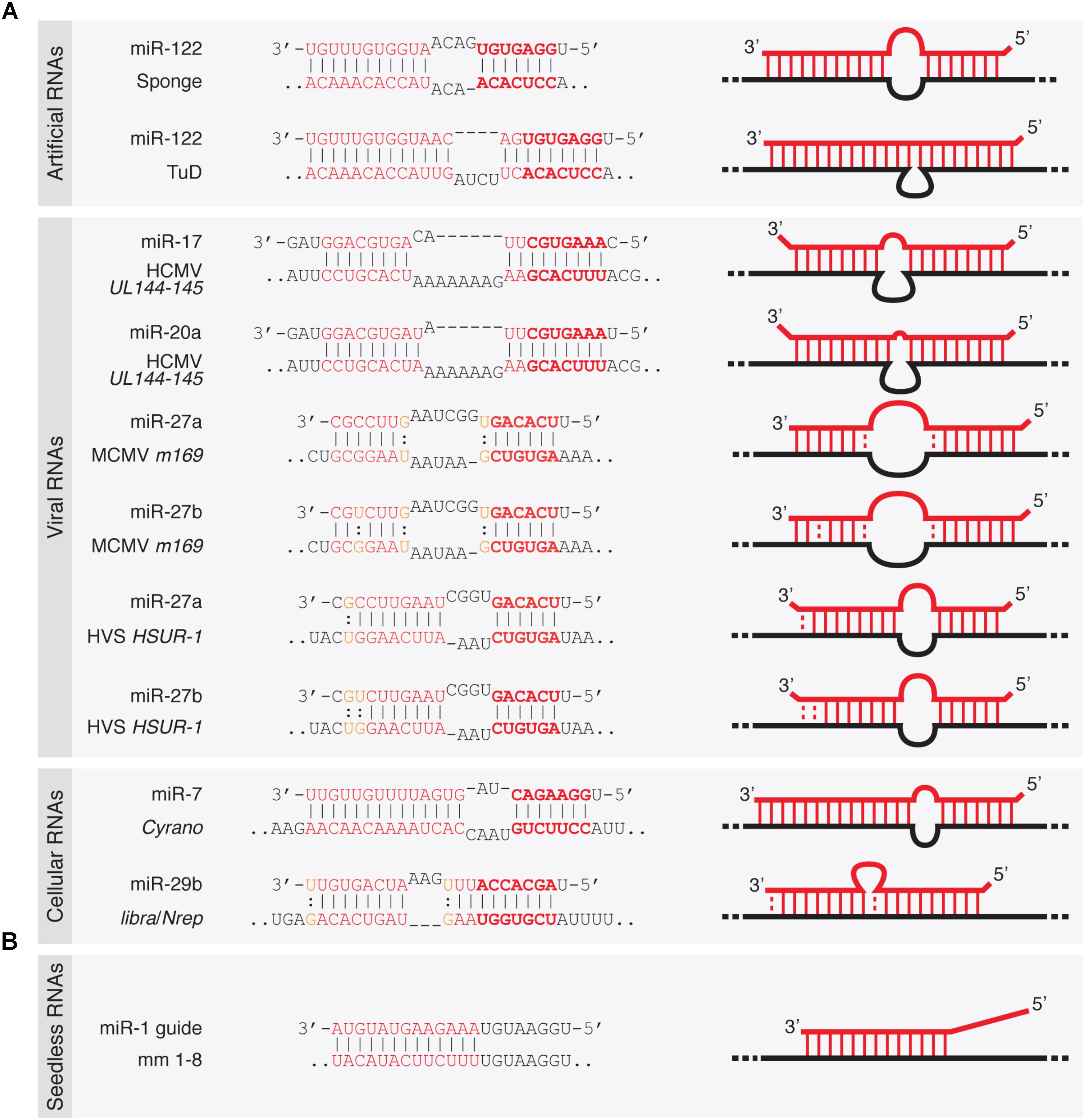
As a result, we identified 48 SNPs in human miRNA seed regions and thousands of SNPs in 3' untranslated regions with the potential to either disturb or create miRNAtarget interactions Furthermore, we experimentally confirmed seven lossoffunction SNPs and one gainoffunction SNP by luciferase assay This is the first case of experimental validation of an SNP in an miRNAコンプリート! seed region Seed region of mirna In addition to our Interactive Map, we will also divide up the Korok Seeds by region Each page below has a full listing of all the Korok Seeds within its region, along with pictures, a description, and a video collecting all the seeds If for whatever reason you prefer this method, or are struggling to get that last seed in spiteNoncanonical sites are sites of interaction between a mRNA and a miRNA that do not involve the canonical pairing in the seed region (positions 2 7) of the miRNA They are of two types A 3' compensatory site is one in which strong 3' pairing (consequential miRNAtarget complementarity outside the seed region) compensates for an imperfect seed match (Friedman et al, 09) A



1




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal
MiRNA sequences present in an exon should be edited through silent point mutations, in the seed region, relative to the open reading frame of the coding gene Intronic miRNAs may be removed if their sequence is not required for proper premRNA splicing, otherwise, point mutations in the seed region should be attempted Following the alteration of a miRNA gene, its expression This indicates that miRNA seed regions might be not so tolerant of genetic variants since most miRNAs have few or rare SNPs in their seed regions Further, we investigated the clustering patterns of the miRNAs with SNPs in their seed regions An interesting observation is that the miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region are significantly enriched in clusters (Figure 1, For the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 × 10 −4, χ 2 test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate the same sets of target genes




Target Recognition By Sirna And Mirna A Sirna Is Usually Fully Download Scientific Diagram



Plos One Micrornas Mir 19 Mir 340 Mir 374 And Mir 542 Regulate Mid1 Protein Expression
MicroRNA editing in seed region aligns with cellular changes in hypoxic conditions RNA editing is a finely tuned, dynamic mechanism for posttranscriptional gene regulation that has been thoroughly investigated in the last decade The impact of miRNA seed types on target downregulation Previous studies have identified several major types of canonical miRNA target sites, including those The miRNA sequence can be separated into five functional domains that affect miRNAtarget recognition 5′ anchor (nt 1), seed sequence (nts 2–8), central region (nts 9–12), 3′ supplementary region (nts 13–16), and 3′ tail (nts 17–22) (Wee et al, 12) We anticipated that complementarity to the seed sequence of the cognate miRNA would be a prominent feature inIn addition to seed regions, miRNA target genes have other features, such as binding free energy, the degree of 1316 bit matching, the sequence conservativeness of miRNA, the exposure of the target point, and so on (Schäfer M, Ciaudo C Prediction of the miRNA interactome–Established methods and upcoming perspectivesJ Computational and structural biotechnology journal,




3 Uridylation Confers Mirnas With Non Canonical Target Repertoires Sciencedirect
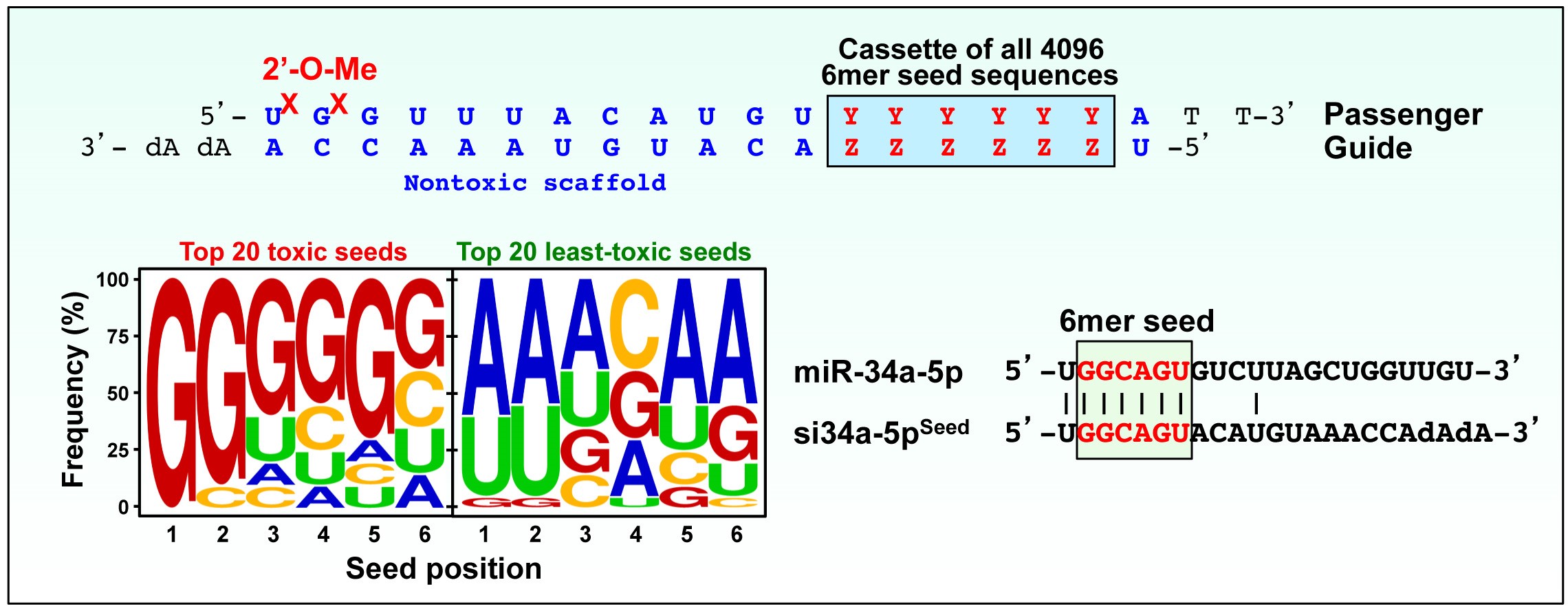



6mer Seed Toxicity A Kill Code Embedded In The Genome Peter Lab Feinberg School Of Medicine Northwestern University
In contrast, the TargetScan algorithm considers only seed regions of miRNA families for greater accuracy To test the sensitivity of target prediction algorithms we used Highthroughput sequencing of RNA isolated by crosslinking immunoprecipitation (HITSCHIPS) Table 1 Number of genes from Ensembl database and miRNAs from miRBase (release 18) in the webserver miRNAMa et al, 13An integrated platform for analyzing the functional impact of genetic polymorphisms in miRNA seed regions and miRNA target sites The browse and search pages of PolymiRTS allow users to explore the relations between the PolymiRTSs and gene expression traits, physiological and behavioral phenotypes, human diseases and biological pathways human;




Multiple Modes Of Mirna Action The Regulation By Mirna On Its Target Download Scientific Diagram



2
6月 17, 21 Seed coat so that water and oxygen can enter the seeds In nature, hard seed coats are cracked or softened by fire, extreme temperatures, digestive acids in the stomachs of animals, or by the abrasion of blowing sand After the seed coat has beenWhen using default settings, TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA (Lewis et al, 05)As options, predictions with only poorly conserved sites and predictions with nonconserved miRNAs are also provided Also, new classes of miRNA were recently described, ie, class of miRNA target sites that lack both perfect seed pairing and 3′compensatory pairing and instead have 11 to 12 contiguous Watson–Crick pairs to the center of the miRNA or class of miRNA recognition elements that function exclusively in coding sequence (CDS) regions Now, 1 of the biggest challenge will



2




Microrna Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms And Diabetes Mellitus A Comprehensive Review Zhang 19 Clinical Genetics Wiley Online Library
The nucleotides 28 in miRNA are termed 'seed,' which is the most crucial region for target recognition The seed region undergoes WatsonCrick base pairing with 3'UTR of mRNAs The degree of mRNA destabilization differs according to the class of the target site The different classes(of target sites to seed) are given below with increasing efficacy and preferential miRNA seed region enrichment in the exosomal lncRNA is independent of sequence length To investigate if sequence length was a determinant in miRNA seed enrichment, we compared the average length of all exosomal lncRNAs to the cellular lncRNAs in each cell line Performing one way ANOVA test, we observed that lncRNAs in the exosomes of VCaP and LNCaPBy investigating its behavior in a dynamic context, we found that miRNA editing events in the seed region are not depended on miRNA expression, unprecedentedly providing insights on the targetome shifts derived from these modifications This reveals that miRNA editing acts under the influence of environmentally induced stimuliOur results show a miRNA editing activity trend




The Characterization Of Microrna Mediated Gene Regulation As Impacted By Both Target Site Location And Seed Match Type



1
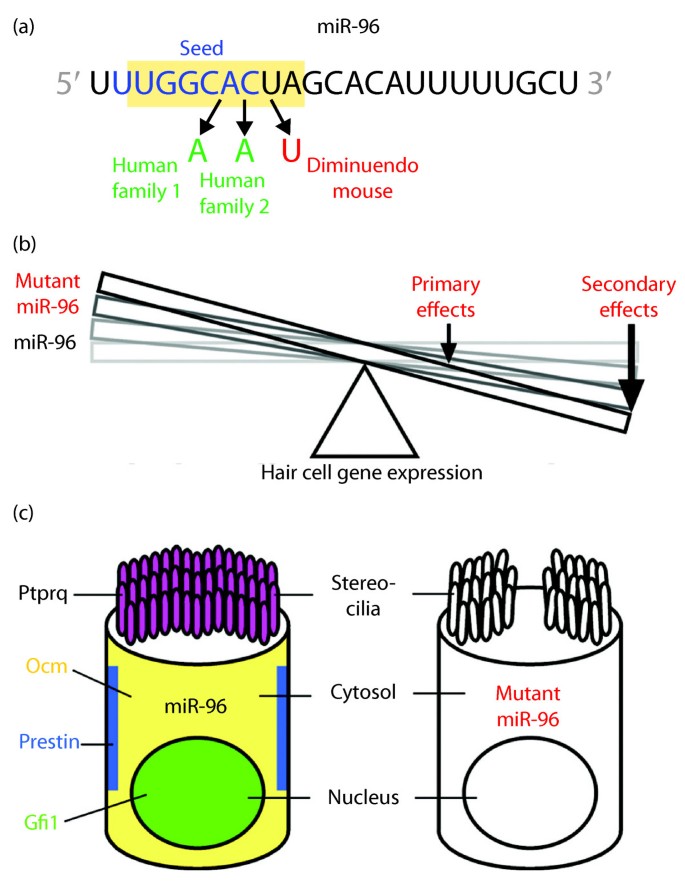
Here we show that point mutations in the seed region of miR96, a miRNA expressed in hair cells of the inner ear 8, result in autosomal dominant, progressive hearing loss This isSeed region of mirna Seed region of mirna A mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing to the 3′ region of the miRNA was not critical for silencing Furthermore, we evaluated theA database of naturally occuring DNA variations in miRNA seed regions and their target sites MosquitoTar miRNA targets in an integrate database for mosquitoes, inclusive of prediction and functional analysis tools Three different algorithms are used to predict miRNA function from overlapping target genes SonamiR Database




Mirna 27b Targets The 3 Utr Of Foxj3 A Sequence Alignment Of Download Scientific Diagram
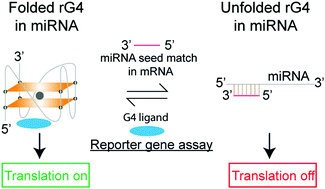



Structural Analysis Reveals The Formation And Role Of Rna G Quadruplex Structures In Human Mature Micrornas Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing




Microrna Gga Mir 6578 Containing Polymorphism Within The Mirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram



2
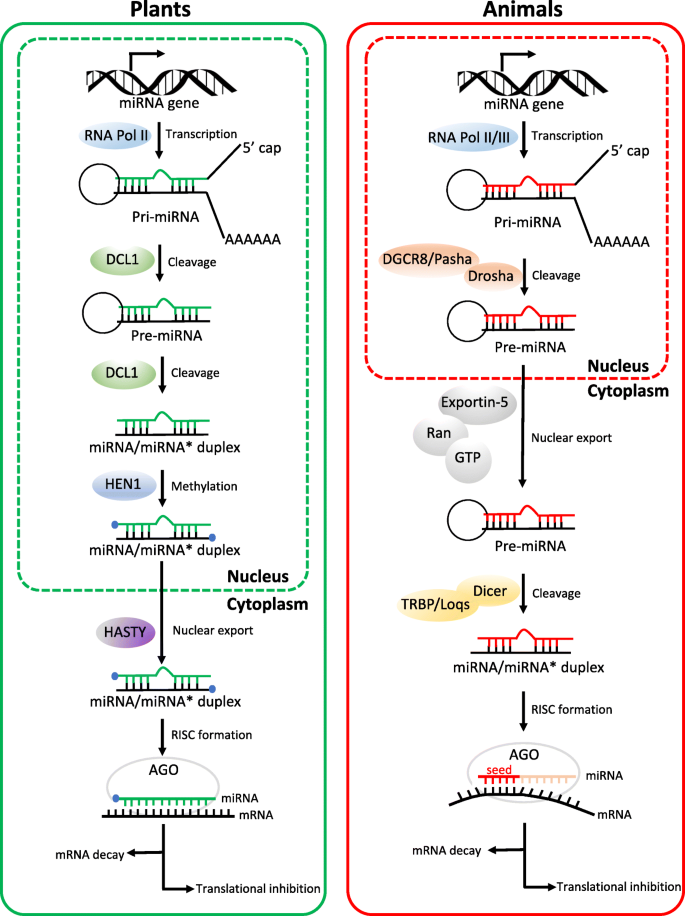



Micrornas From Plants To Animals Do They Define A New Messenger For Communication Nutrition Metabolism Full Text



Plos Computational Biology Miraw A Deep Learning Based Approach To Predict Microrna Targets By Analyzing Whole Microrna Transcripts




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Abstract Europe Pmc




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal
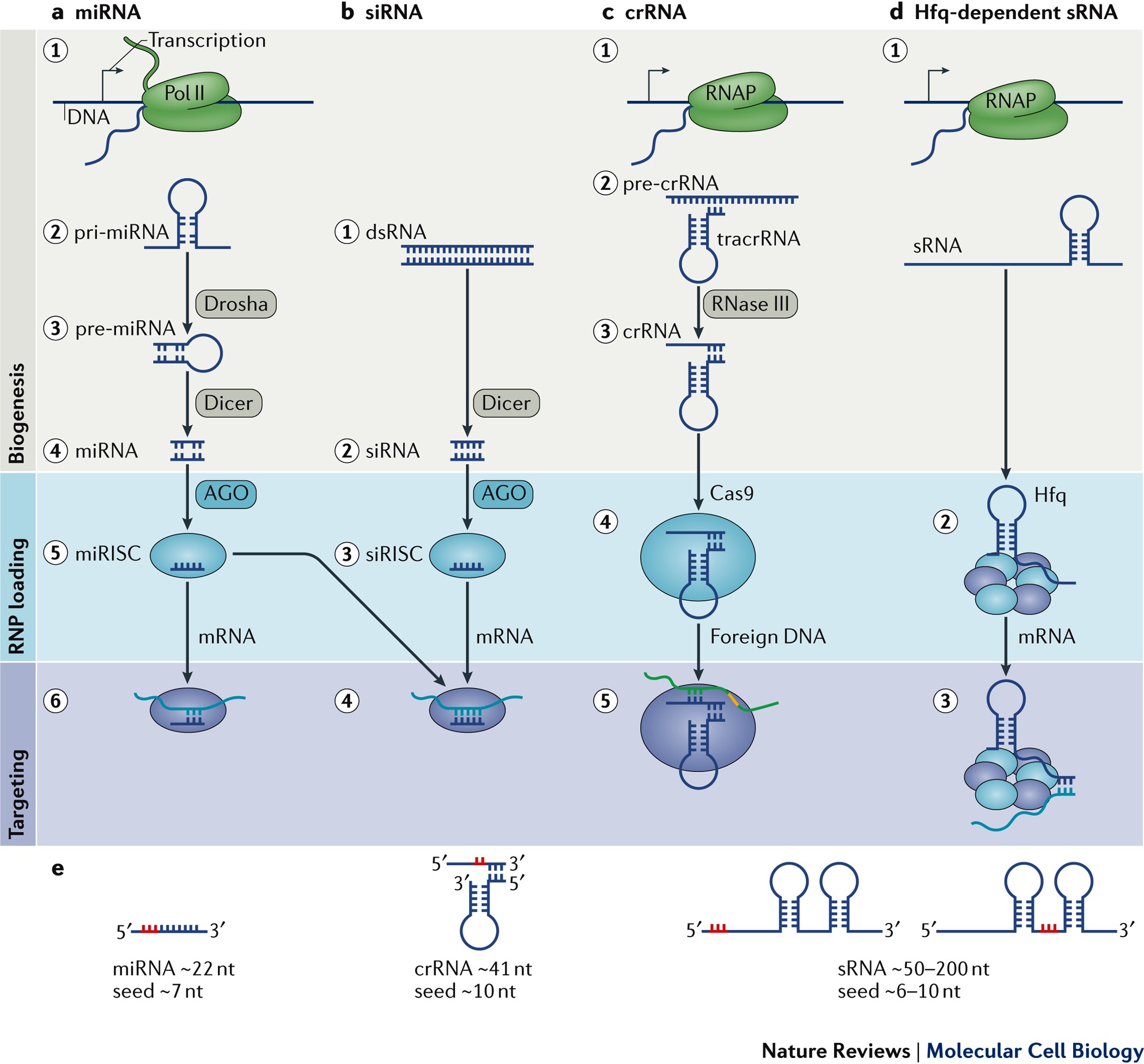



Rna Based Recognition And Targeting Sowing The Seeds Of Specificity Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology




Metazoan Micrornas Sciencedirect




Mirna Targeting Growing Beyond The Seed Trends In Genetics



Microrna Wikipedia




Human Polymorphism At Micrornas And Microrna Target Sites Pnas
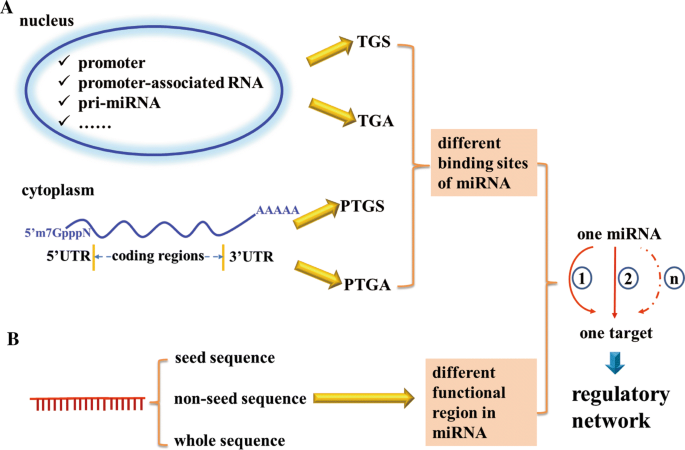



Regulatory Network Of Mirna On Its Target Coordination Between Transcriptional And Post Transcriptional Regulation Of Gene Expression Springerlink




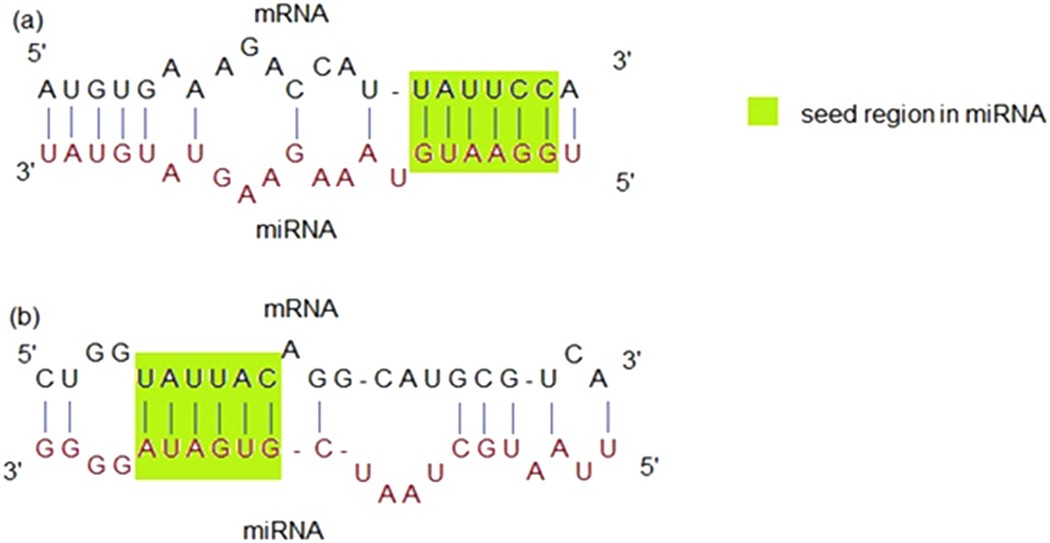
Examples Of Mirna Target Interactions Pairing Schemes Of Several Download Scientific Diagram



Plos One Altered Gene Expression Associated With Microrna Binding Site Polymorphisms



Plos One Microrna Seed Region Length Impact On Target Messenger Rna Expression And Survival In Colorectal Cancer




Chemical Modifications In The Seed Region Of Mirnas 221 222 Increase The Silencing Performances In Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells Sciencedirect




Here S A Topic We Applied Biological Materials Abm Facebook



1
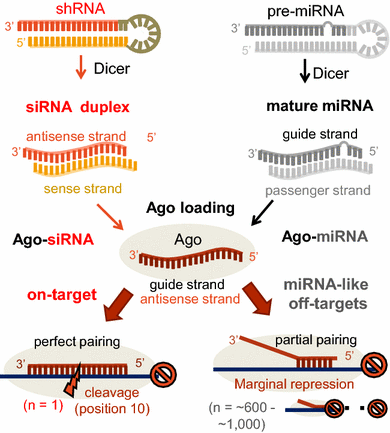



Evaluation And Control Of Mirna Like Off Target Repression For Rna Interference Springerlink




Mirna Seed Regions Are Defined By Structural Backbone Rigidity A Download Scientific Diagram
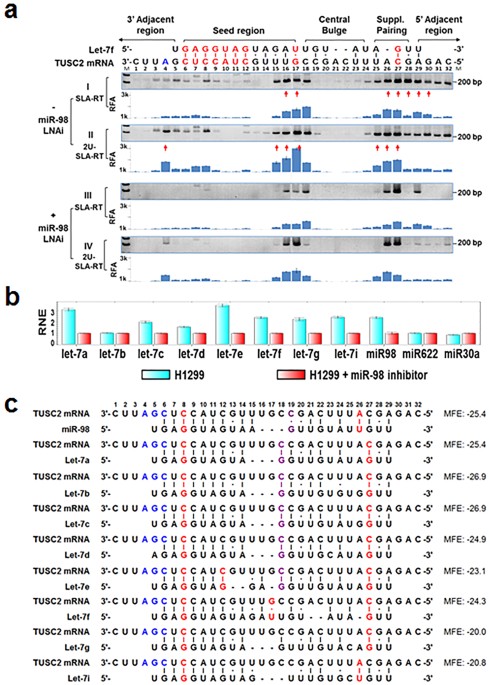



Microrna Mediated Target Mrna Cleavage And 3 Uridylation In Human Cells Scientific Reports



2




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences




Mirpro A Novel Standalone Program For Differential Expression And Variation Analysis Of Mirnas Scientific Reports




Introduction Of 2 6 Diaminopurines Into Serinol Nucleic Acid Improves Anti Mirna Performance Kamiya 17 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library
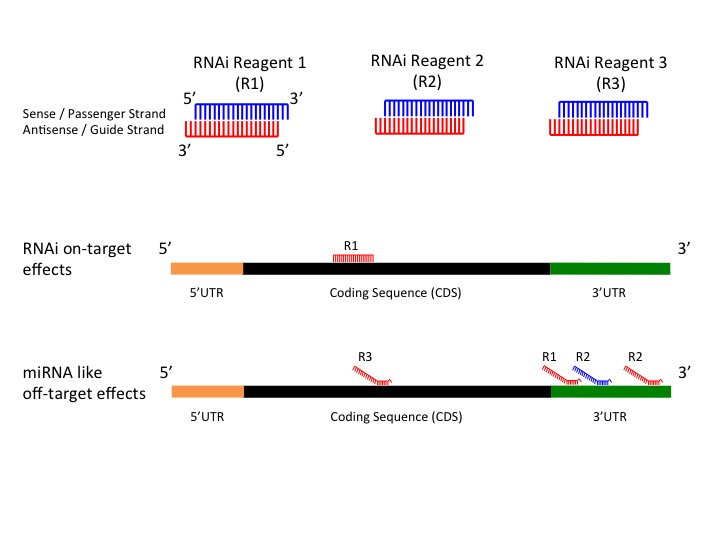



Gess




Common Features Of Microrna Target Prediction Tools Abstract Europe Pmc




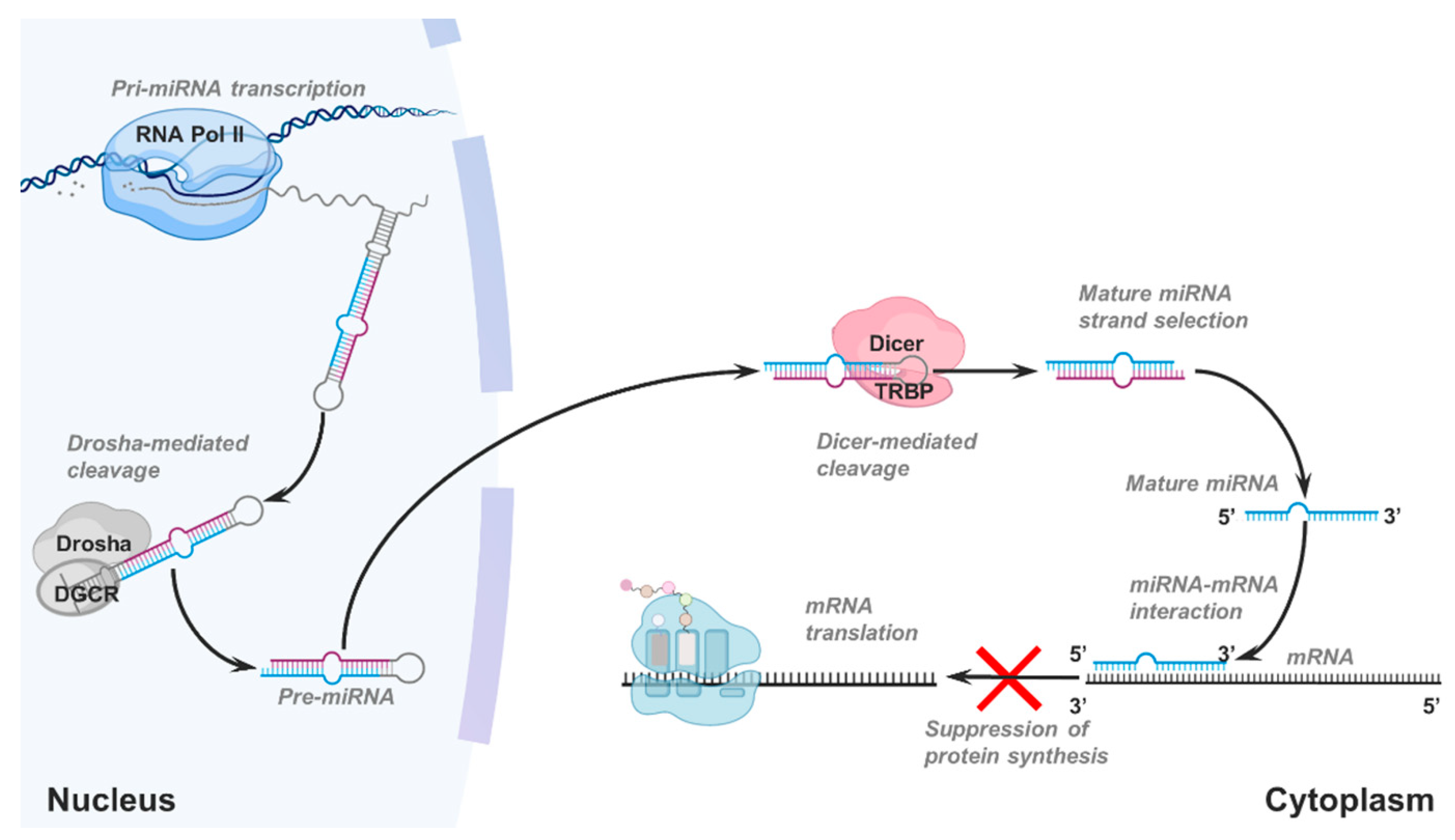
Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow




Microrna Polymorphisms The Future Of Pharmacogenomics Molecular Epidemiology And Individualized Medicine Pharmacogenomics




Types Of Microrna Target Sites A There Are Three Types Of Canonical Download Scientific Diagram




A Study Of Micrornas In Silico And In Vivo Bioimaging Of Microrna Biogenesis And Regulation Kim 09 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library




Microrna Regulation And Cardiac Calcium Signaling Circulation Research



Micrornas In Skin Biology Biogenesis Regulations And Functions In Homeostasis And Diseases




A Cartoon Showing The Site And Mechanism Of Mirna Targeting To Mrna Download Scientific Diagram




Function Control Of Anti Microrna Oligonucleotides Using Interstrand Cross Linked Duplexes Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



Advances In Multiplexed Techniques For The Detection And Quantification Of Micrornas Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing



2




Rna Targeting Utilizing Pairing Outside Of The Canonical Mirna 5 Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell




Sites Matching In The Mirna Seed Region Including All K Mer 8mer Download Scientific Diagram




Types Of Mirna Target Sites And Multiple Sites A Stringent Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Ijms Free Full Text Microrna Nanotherapeutics For Lung Targeting Insights Into Pulmonary Hypertension Html
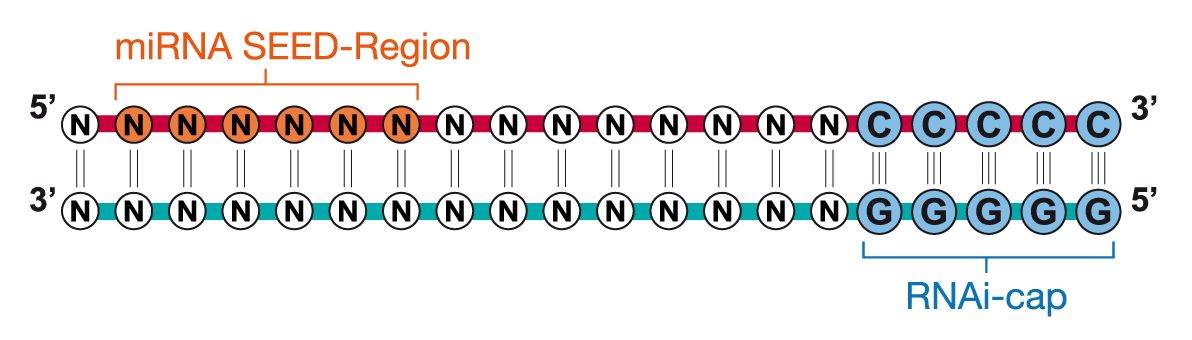



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




Unambiguous Identification Of Mirna Target Site Interactions By Different Types Of Ligation Reactions Sciencedirect



Variability In Porcine Microrna Genes And Its Association With Mrna Expression And Lipid Phenotypes Genetics Selection Evolution Full Text




Microrna Gga Mir 6578 Containing Polymorphism Within The Mirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram



Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports




Rna Mrna Target Interaction Schematic Overview Of A Mirna Interaction Download Scientific Diagram




Crispr Screening Strategies For Microrna Target Identification Yang The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics




Zk29d9tfhfudmm
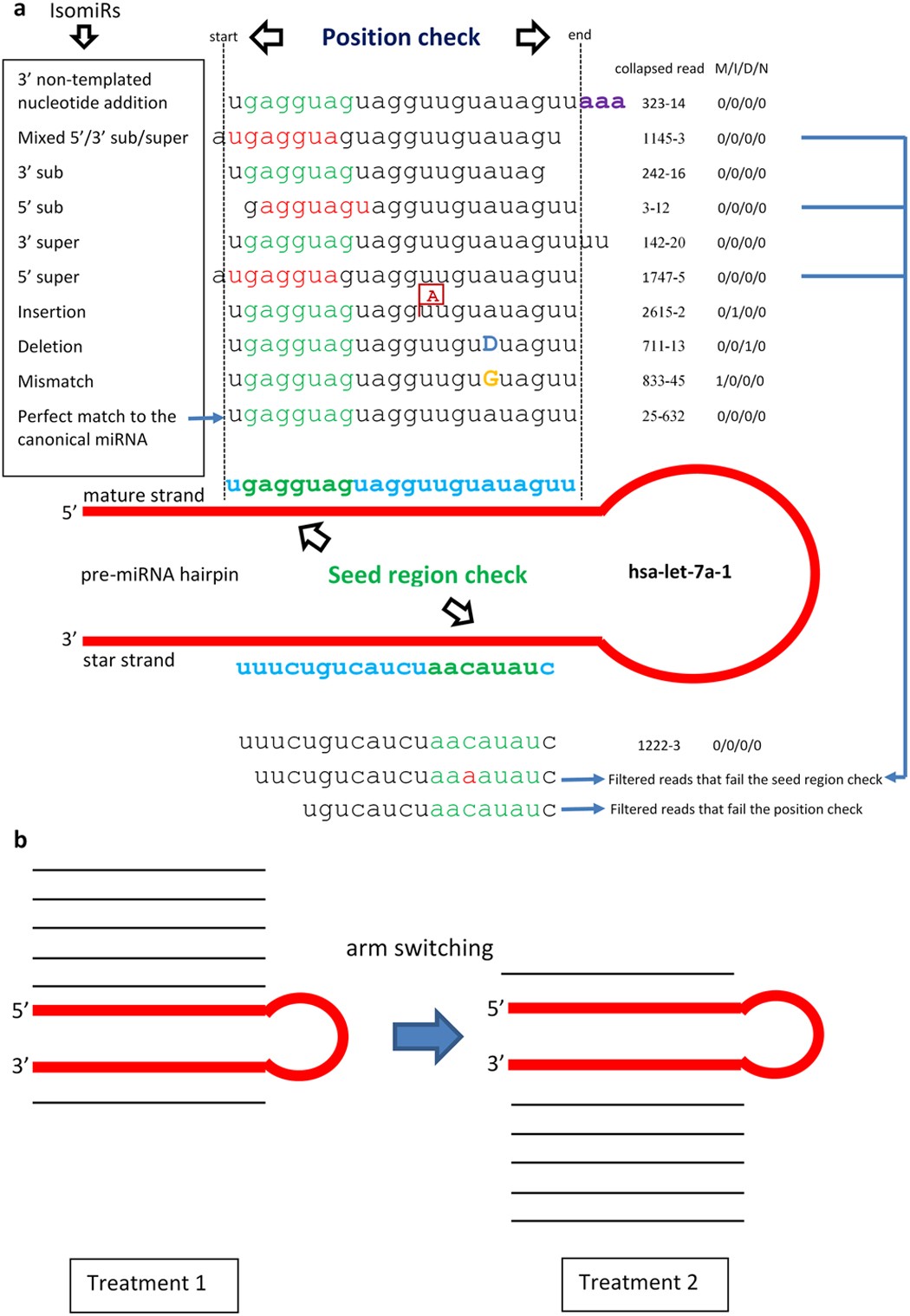



Mirpro A Novel Standalone Program For Differential Expression And Variation Analysis Of Mirnas Scientific Reports




Microrna 92a Regulates The Expression Of Aphid Bacteriocyte Specific Secreted Protein 1 Bmc Research Notes Full Text
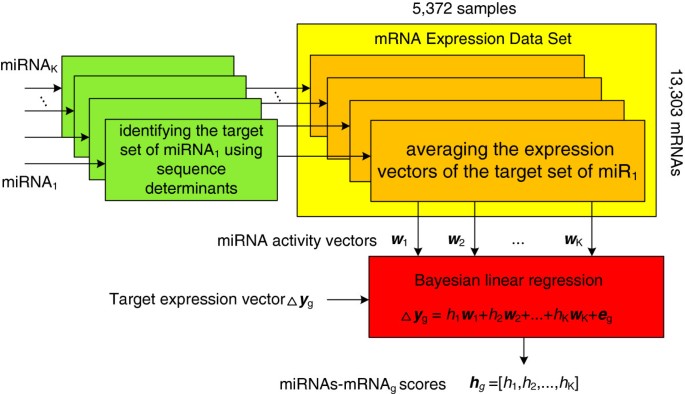



Baymir Inferring Evidence For Endogenous Mirna Induced Gene Repression From Mrna Expression Profiles Bmc Genomics Full Text




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal
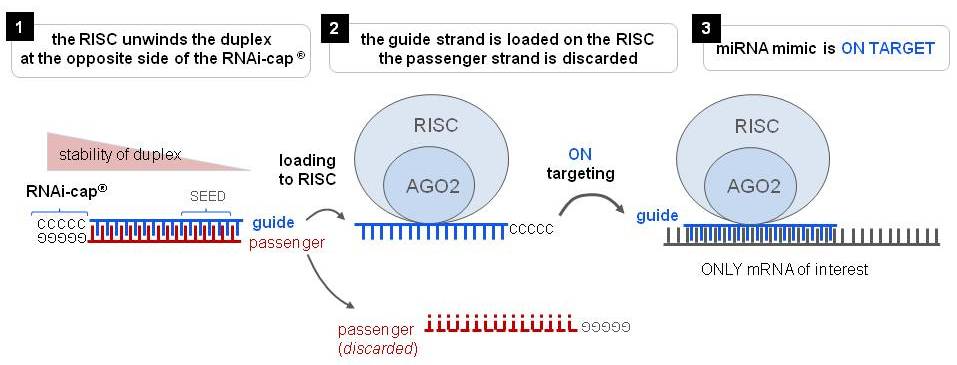



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna
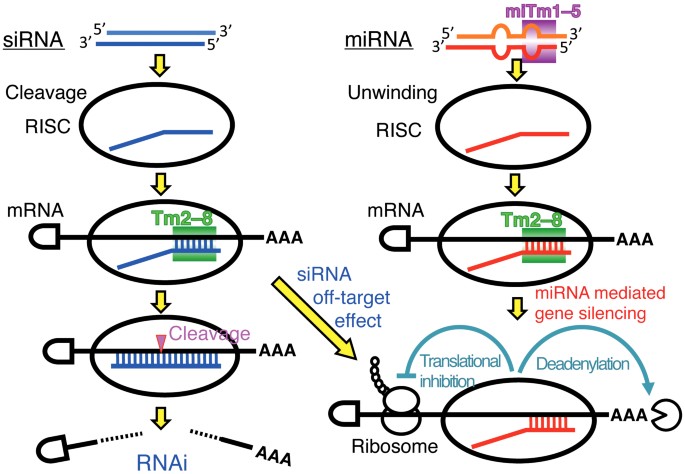



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports



2




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram




Different Seed Match Regions Of Mirnas Mirnalyze Follows A Download Scientific Diagram



Mirna Workshop Mirna Target Prediction In Animals Ppt Download




Microrna Wikipedia
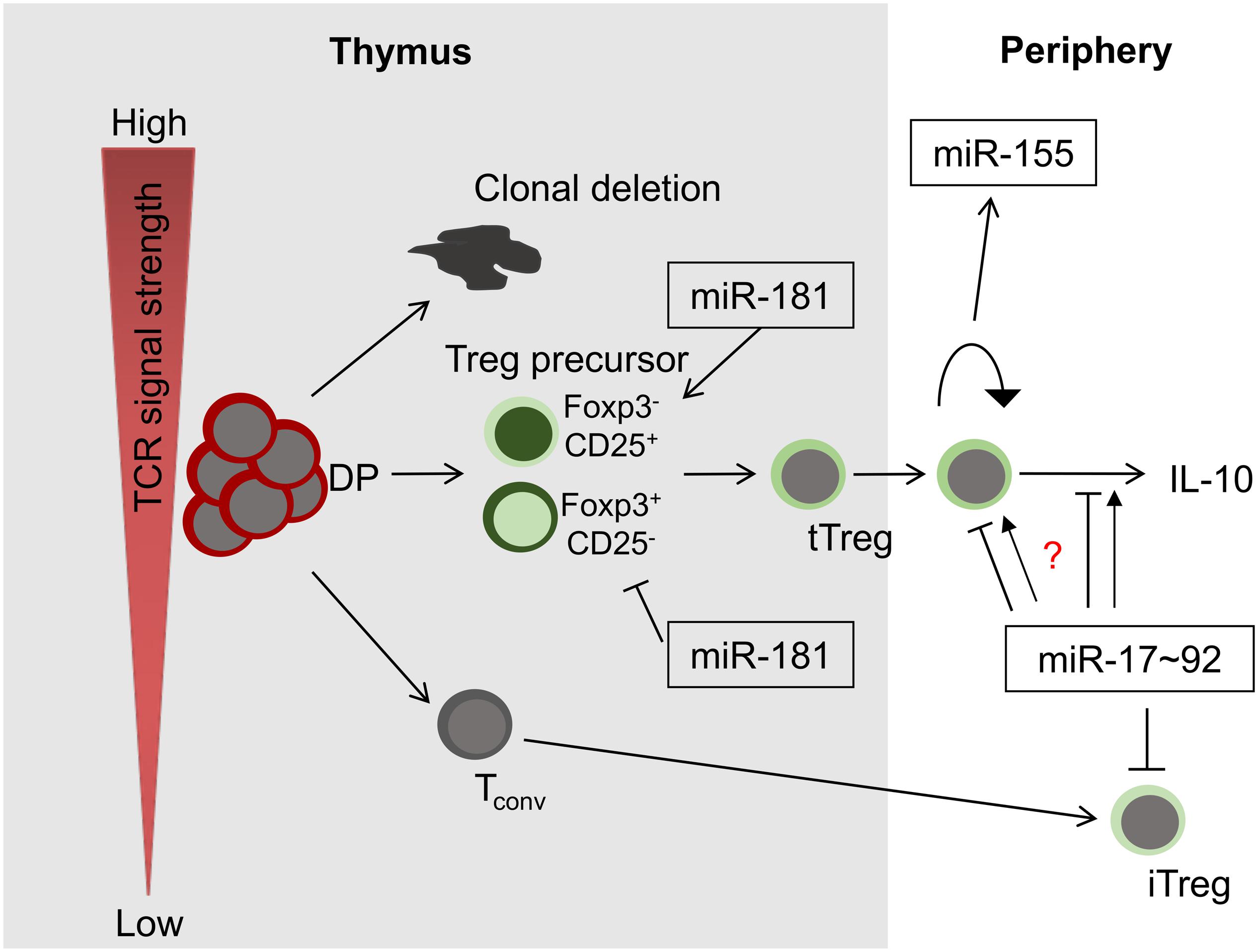



Frontiers The Role Of Micrornas In Development And Function Of Regulatory T Cells Lessons For A Better Understanding Of Microrna Biology Immunology



Micrornas Recent Insights Towards Their Role In Male Infertility And Reproductive Cancers Bosnian Journal Of Basic Medical Sciences




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Mirna Introduction Biogenesis Nomenclature And Experimental Workflow



Targetscan Non Canonical Sites




Mirna Mirna Targets Functional Analysis



Mirna



Micrornas Sound Off Genome Medicine Full Text



New Insights Into The Function Of Mammalian Argonaute2




6mer Seed Toxicity In Viral Micrornas Sciencedirect
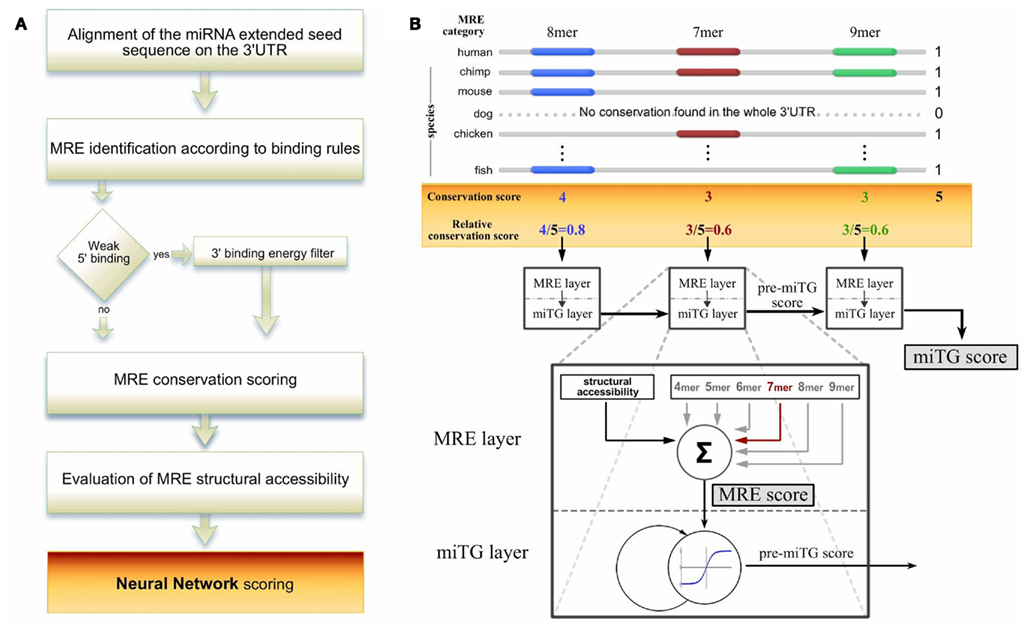



Frontiers Accurate Microrna Target Prediction Using Detailed Binding Site Accessibility And Machine Learning On Proteomics Data Genetics




Prediction Of The Mirna Interactome Established Methods And Upcoming Perspectives Sciencedirect




Got Target Computational Methods For Microrna Target Prediction And Their Extension Abstract Europe Pmc
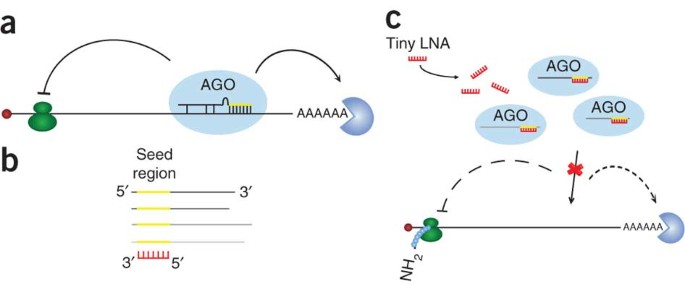



Silencing Of Microrna Families By Seed Targeting Tiny Lnas Nature Genetics




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram



Plos Computational Biology Miraw A Deep Learning Based Approach To Predict Microrna Targets By Analyzing Whole Microrna Transcripts



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿